MauriceGit / Skiplist
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Skiplist
Fast Skiplist Implementation
This Go-library implements a very fast and efficient Skiplist that can be used as direct substitute for a balanced tree or linked list.
All basic operations ( Find, Insert and Delete) have approximate runtimes of O(log(n)) that prove real in benchmarks.
For detailed API documentation, see the official docs: godoc.org/github.com/MauriceGit/skiplist.
This implementation introduces a minimum amount of overhead and is tailored for maximum performance across all operations. In benchmarks, this skiplist is currently the fastest implementation in Go known to me. See a thorough benchmark of multiple skiplist implementations at: github.com/MauriceGit/skiplist-survey.
Find, Insert, Delete at both ends of the SkipList
Y-Axis is measured in nanoseconds per operation for all charts
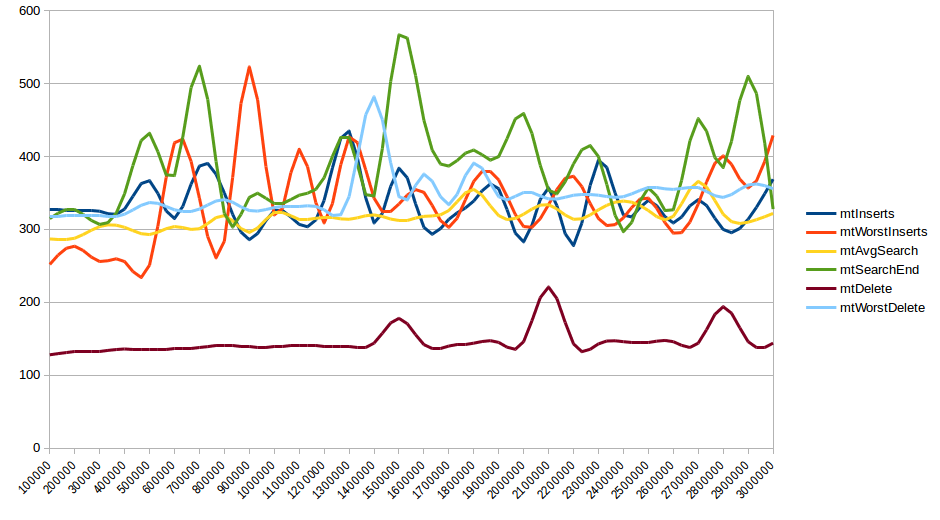 All functions, be it
All functions, be it Find, Insert or Delete that operate on first or last elements in the skiplist behave in near Constant time, no matter how many
elements are already inserted in the skiplist.
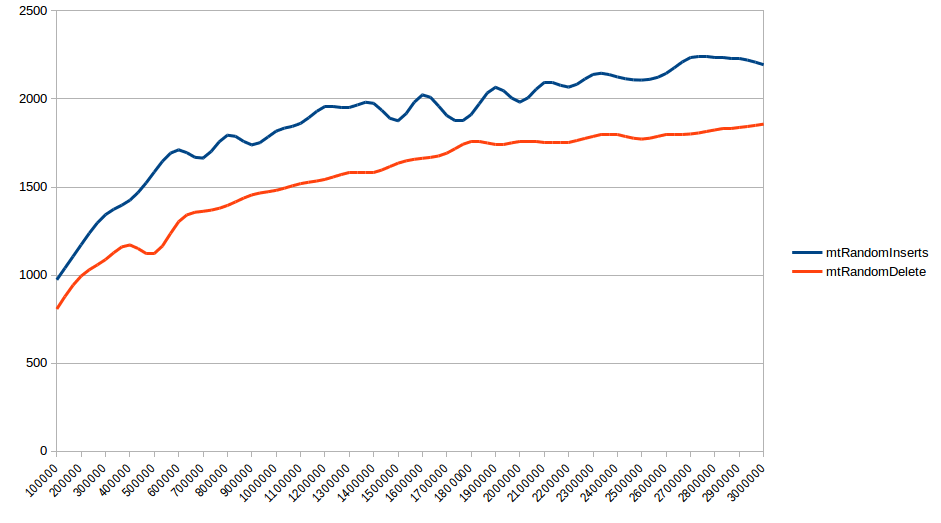 For real-world cases where elements are inserted or removed at random positions in the skiplist, we can clearly see the approximate O(log(n)) behaviour of the
implementation which approximates to a constant value around 1800ns for
For real-world cases where elements are inserted or removed at random positions in the skiplist, we can clearly see the approximate O(log(n)) behaviour of the
implementation which approximates to a constant value around 1800ns for Delete and 2200ns for Insert.
Comparison to other Skiplist implementations
The following graphs are taken from github.com/MauriceGit/skiplist-survey. Please visit this skiplist survey for a much more detailed comparison over several benchmarks between different skiplist implementations.
Overall, this implementation is the fastest skiplist for nearly all operations. Especially for real-world applications.
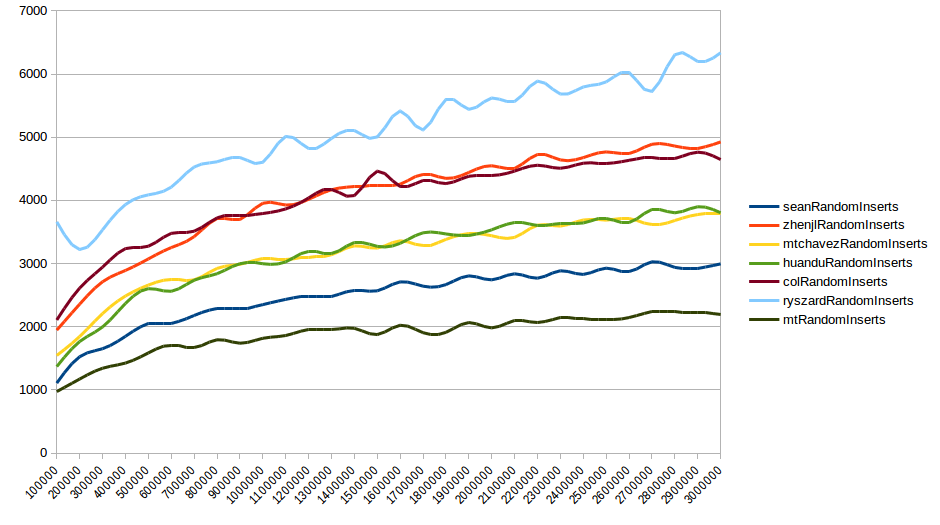 If we compare random insertions of this skiplist to other implementations, it is clearly the fastest by up to 800ns per insertion for up to 3m elements.
If we compare random insertions of this skiplist to other implementations, it is clearly the fastest by up to 800ns per insertion for up to 3m elements.
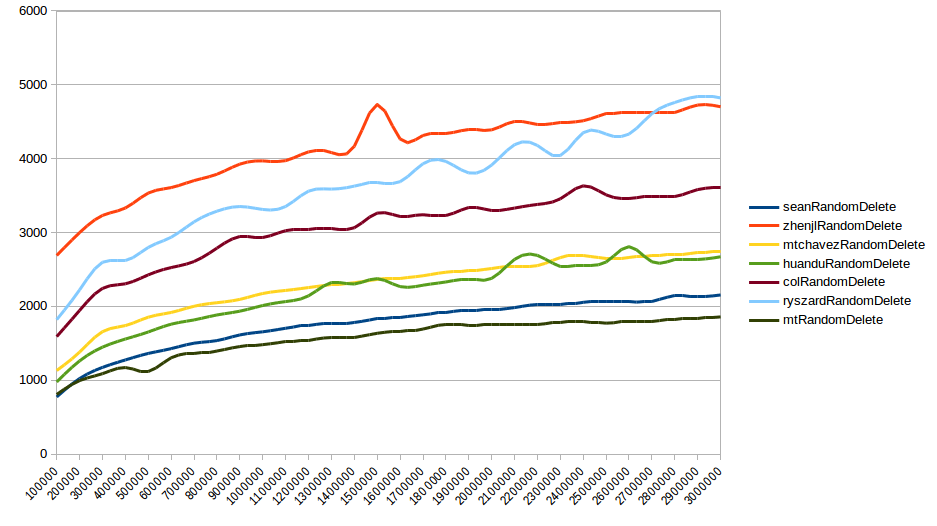 If we compare random deletions of this skiplist to other implementations, it is clearly the fastest by up to 300ns per deletion for up to 3m elements.
If we compare random deletions of this skiplist to other implementations, it is clearly the fastest by up to 300ns per deletion for up to 3m elements.
Usage
import (
"github.com/MauriceGit/skiplist"
"fmt"
)
type Element int
// Implement the interface used in skiplist
func (e Element) ExtractKey() float64 {
return float64(e)
}
func (e Element) String() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%03d", e)
}
func main() {
list := New()
// Insert some elements
for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
list.Insert(Element(i))
}
// Find an element
if e, ok := list.Find(Element(53)); ok {
fmt.Println(e)
}
// Delete all elements
for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
list.Delete(Element(i))
}
}
Convenience functions
Other than the classic Find, Insert and Delete, some more convenience functions are implemented that makes this skiplist implementation very easy and straight forward to use
in real applications. All complexity values are approximates, as skiplist can only approximate runtime complexity.
| Function | Complexity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Find | O(log(n)) | Finds an element in the skiplist |
| FindGreaterOrEqual | O(log(n)) | Finds the first element that is greater or equal the given value in the skiplist |
| Insert | O(log(n)) | Inserts an element into the skiplist |
| Delete | O(log(n)) | Deletes an element from the skiplist |
| GetSmallestNode | O(1) | Returns the smallest element in the skiplist |
| GetLargestNode | O(1) | Returns the largest element in the skiplist |
| Prev | O(1) | Given a skiplist-node, it returns the previous element (Wraps around and allows to linearly iterate the skiplist) |
| Next | O(1) | Given a skiplist-node, it returns the next element (Wraps around and allows to linearly iterate the skiplist) |
| ChangeValue | O(1) | Given a skiplist-node, the actual value can be changed, as long as the key stays the same (Example: Change a structs data) |
