IBM / Spark Tpc Ds Performance Test
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Spark Tpc Ds Performance Test
Explore Spark SQL and its performance using TPC-DS workload
Data Science Experience is now Watson Studio. Although some images in this code pattern may show the service as Data Science Experience, the steps and processes will still work.
Apache Spark is a popular distributed data processing engine that is built around speed, ease of use and sophisticated analytics, with APIs in Java, Scala, Python, R, and SQL. Like other data processing engines, Spark has a unified optimization engine that computes the optimal way to execute a workload with the main purpose of reducing the disk IO and CPU usage.
We can evaluate and measure the performance of Spark SQL using the TPC-DS benchmark. TPC-DS is a widely used industry standard decision support benchmark that is used to evaluate performance of data processing engines. Given that TPC-DS exercises some key data warehouse features, running TPC-DS successfully reflects the readiness of Spark in terms of addressing the need of a data warehouse application. Apache Spark v2.0 supports all the ninety-nine decision support queries that is part of this TPC-DS benchmark.
This Code Pattern is aimed at helping Spark developers quickly setup and run the TPC-DS benchmark in their own development setup.
When the reader has completed this Code Pattern, they will understand the following:
- How to setup the TPC-DS toolkit
- How to generate TPC-DS datasets at different scale factor
- How to create Spark database artifacts
- How to run TPC-DS benchmark queries on Spark in local mode and see the results
- Things to consider when increasing the data scale and run against a spark cluster
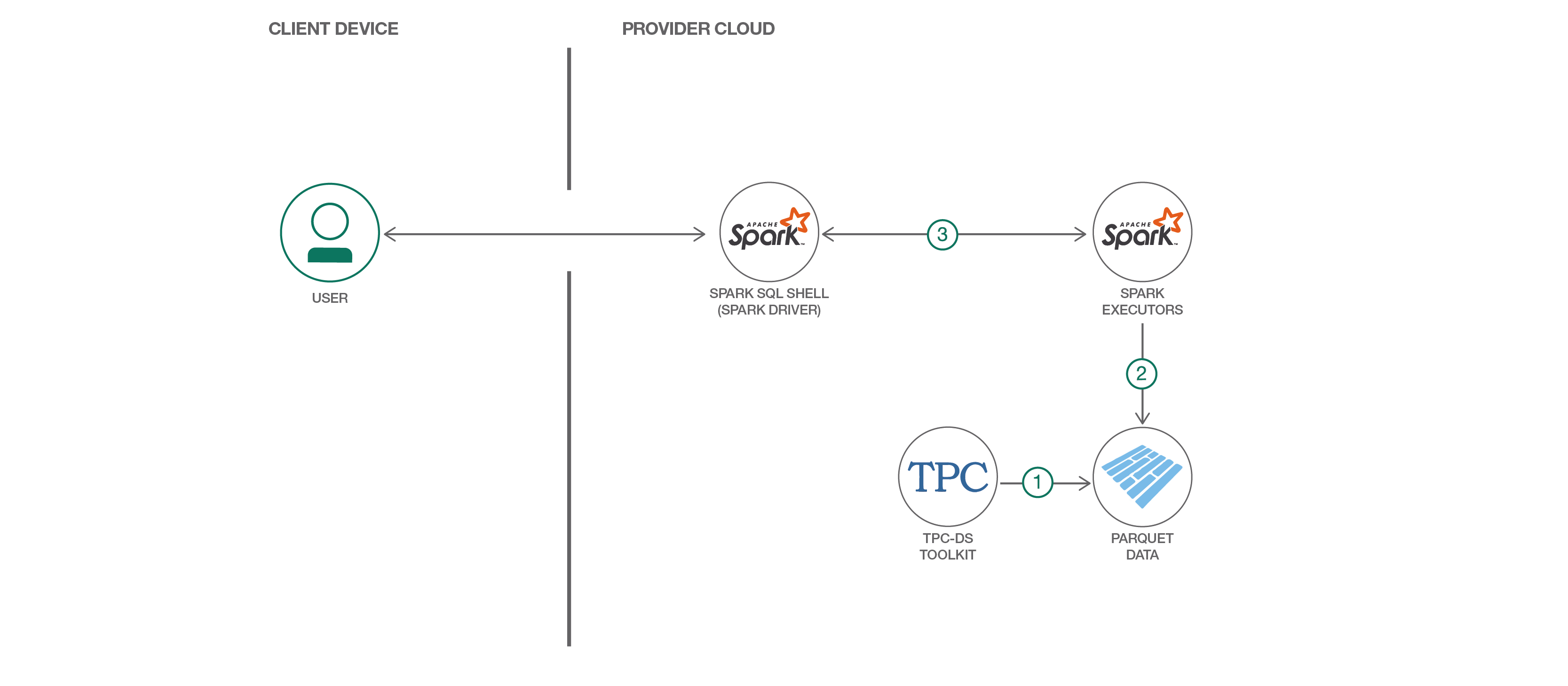
Flow
- Commandline
- Create the spark tables with pre-generated dataset.
- Run the entire query set or a subset of queries and monitor the results.
- Notebook
- Create the spark tables with pre-generated dataset.
- Run the entire query set or individual query.
- View the query results or performance summary.
- View the performance graph.
Included components
- Apache Spark: An open-source, fast and general-purpose cluster computing system
- Jupyter Notebook: An open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and explanatory text.
Featured technologies
- Data Science: Systems and scientific methods to analyze structured and unstructured data in order to extract knowledge and insights.
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence can be applied to disparate solution spaces to deliver disruptive technologies.
- Python: Python is a programming language that lets you work more quickly and integrate your systems more effectively.
Steps
There are two modes of exercising this Code Pattern:
- Run locally using a simple interactive command line shell script.
- Run using a Jupyter notebook in Watson Studio.
Run locally
1. Clone the repository
Clone the spark-tpc-ds-performance-test repo locally. In a terminal, run:
$ git clone https://github.com/IBM/spark-tpc-ds-performance-test
2. Setup development tools (Optional)
Due to licensing restrictions, the TPCDS toolkit is not included as part of the code pattern. Instead, a pre-generated data set with 1GB scale factor is included in this pattern. If you want to work with a data set with larger scale factor or explore learning the full life sycle of setting up TPCDS, you can download the tool kit from TPC-DS and compile in your development environment.
Make sure the required development tools are installed in your platform. This Code Pattern is supported on Mac and Linux platforms only. Depending on your platform, run the following command to install the necessary development tools:
-
Ubuntu:
$ sudo apt-get install gcc make flex bison byacc git -
CentOS/RHEL:
$ sudo yum install gcc make flex bison byacc git -
MacOS:
$ xcode-select --install
To compile the toolkit you need to the following :
unzip <downloaded-tpc-ds-zipfile>
cd <tpc-ds-toolkit-version>/tools
make clean
make OS=<platform>
3. Install Spark
To successfully run the TPC-DS tests, Spark must be installed and pre-configured to work with an Apache Hive metastore.
Perform 1 or more of the following options to ensure that Spark is installed and configured correctly. Once completed, modify bin/tpcdsenv.sh to set SPARK_HOME pointing to your Spark installation directory.
Option 1 - If you already have Spark installed, complete the following steps to ensure your Spark version is properly configured:
$ cd $SPARK_HOME
$ bin/spark-shell
// Enter the following command at the scala prompt
scala> spark.conf
scale> spark.conf.get("spark.sql.catalogImplementation")
res5: String = hive
scala> <ctrl-c>
Note: You must exit out of the spark-shell process or you will encounters errors when performing the TPC-DS tests.
If the prompt returns String = hive, then your installation is properly configured.
Option 2 - If you don't have an installed Spark version, or your current installation is not properly configured, we suggest trying to pull down version 2.2.0 from the Spark downloads page. This version should be configured to work with Apache Hive, but please run the test in the previous option to make sure.
Option 3 - The last option available is it to download and build it yourself. The first step is to clone the Spark repo:
$ git clone https://github.com/apache/spark.git
Then build it using these instructions. Please make sure to build Spark with Hive support by following the Building With Hive and JDBC Support section.
4. Run the script
Note: Verify that the bin/tpcdsenv.sh script has SPARK_HOME setup correctly.
Now that we have Spark setup and the TPC-DS scripts downloaded, we are ready to setup and start running the TPC-DS queries using the bin/tpcdsspark.sh utility script. This driver script will allow you to compile the TPC-DS toolkit to produce the data and the queries, and then run them to collect results.
Perform the following steps to complete the execution of the script:
$ cd spark-tpc-ds-performance-test
$ bin/tpcdsspark.sh
==============================================
TPC-DS On Spark Menu
----------------------------------------------
SETUP
(1) Create spark tables
RUN
(2) Run a subset of TPC-DS queries
(3) Run All (99) TPC-DS Queries
CLEANUP
(4) Cleanup
(Q) Quit
----------------------------------------------
Please enter your choice followed by [ENTER]:
Setup Option: "(1) - Create Spark Tables"
This option creates the tables in the database name specified by TPCDS_DBNAME defined in bin/tpcdsenv.sh. The default name is TPCDS but can be changed if needed. The created tables are based on the pre-generated data.
The SQL statements to create the tables can be found in src/ddl/individual, and are created in parquet format for efficient processing.
Due to licensing restrictions, the TPCDS toolkit is not included as part of the code pattern. Instead, a pre-generated data set with 1GB scale factor is included in this pattern. If you want to work with a data set with larger scale factor or explore learning the full life sycle of setting up TPCDS, you can download the tool kit from TPC-DS and compile in your development environment. Here are the instructions that describes how to compile the tool kit and generate data.
-
Compile the toolkit
unzip <downloaded-tpc-ds-zipfile> cd <tpc-ds-toolkit-version>/tools make clean make OS=<platform> # (platform can be 'macos' or 'linux'). -
Generate the data.
cd <tpc-ds-toolkit-version>/src/toolkit/tools ./dsdgen -dir <data_gen_dir> -scale <scale_factor> -verbose y -terminate n # data_gen_dir => The output directory where data will be generated at. # scale_factor => The scale factor of data. -
Generate the queries.
The
dsqgenutility in the tpcds toolkit may be used to generate the queries. Appropiate options should be passed to this utility. A typical example of its usage is:cd <tpc-ds-toolkit-version>/tools ./dsqgen -VERBOSE Y -DIALECT <dialectname> -DIRECTORY <query-template-dir> -SCALE <scale-factor> -OUTPUT_DIR <output-dir>
Below is example output for when this option is chosen.
==============================================
TPC-DS On Spark Menu
----------------------------------------------
SETUP
(1) Create spark tables
RUN
(2) Run a subset of TPC-DS queries
(3) Run All (99) TPC-DS Queries
CLEANUP
(4) Cleanup
(Q) Quit
----------------------------------------------
Please enter your choice followed by [ENTER]: 1
----------------------------------------------
INFO: Creating tables. Will take a few minutes ...
INFO: Progress : [########################################] 100%
INFO: Spark tables created successfully..
Press any key to continue
Run Option: "(2) - Run a subset of TPC-DS queries"
A comma separated list of queries can be specified in this option. The result of each query in the supplied list is generated in TPCDS_WORK_DIR, with a default directory location of work. The format of the result file is query<number>.res.
A summary file named run_summary.txt is also generated. It contains information about query number, execution time and number of rows returned.
Note: The query number is a two digit number, so for query 1 the results will be in query01.res.
Note: If you are debugging and running queries using this option, make sure to save run_summary.txt after each of your runs.
==============================================
TPC-DS On Spark Menu
----------------------------------------------
SETUP
(1) Create spark tables
RUN
(2) Run a subset of TPC-DS queries
(3) Run All (99) TPC-DS Queries
CLEANUP
(4) Cleanup toolkit
(Q) Quit
----------------------------------------------
Please enter your choice followed by [ENTER]: 2
----------------------------------------------
Enter a comma separated list of queries to run (ex: 1, 2), followed by [ENTER]:
1,2
INFO: Checking pre-reqs for running TPC-DS queries. May take a few seconds..
INFO: Checking pre-reqs for running TPC-DS queries is successful.
INFO: Running TPCDS queries. Will take a few minutes depending upon the number of queries specified..
INFO: Progress : [########################################] 100%
INFO: TPCDS queries ran successfully. Below are the result details
INFO: Individual result files: spark-tpc-ds-performance-test/work/query<number>.res
INFO: Summary file: spark-tpc-ds-performance-test/work/run_summary.txt
Press any key to continue
Run Option: "(3) - Run all (99) TPC-DS queries"
The only difference between this and option (5) is that all 99 TPC-DS queries are run instead of a subset.
Note: If you are running this on your laptop, it can take a few hours to run all 99 TPC-DS queries.
==============================================
TPC-DS On Spark Menu
----------------------------------------------
SETUP
(1) Create spark tables
RUN
(2) Run a subset of TPC-DS queries
(3) Run All (99) TPC-DS Queries
CLEANUP
(4) Cleanup toolkit
(Q) Quit
----------------------------------------------
Please enter your choice followed by [ENTER]: 3
----------------------------------------------
INFO: Checking pre-reqs for running TPC-DS queries. May take a few seconds..
INFO: Checking pre-reqs for running TPC-DS queries is successful.
INFO: Running TPCDS queries. Will take a few minutes depending upon the number of queries specified..
INFO: Progress : [########################################] 100%
INFO: TPCDS queries ran successfully. Below are the result details
INFO: Individual result files: spark-tpc-ds-performance-test/work/query<number>.res
INFO: Summary file: spark-tpc-ds-performance-test/work/run_summary.txt
Press any key to continue
Cleanup option: "(4) - Cleanup"
This will clean up all of the files generated during option steps 1, 2, and 3. If you use this option, make sure to run the setup steps (1) before running queries using option 2 and 3.
Cleanup option: "(Q) - Quit"
This will exit the script.
Run using a Jupyter notebook in Watson Studio
1. Sign up for Watson Studio
Sign up for IBM's Watson Studio. By creating a project in Watson Studio a free tier Object Storage service will be created in your IBM Cloud account.
Note: When creating your Object Storage service, select the
Freestorage type in order to avoid having to pay an upgrade fee.
Take note of your service names as you will need to select them in the following steps.
2. Create the notebook
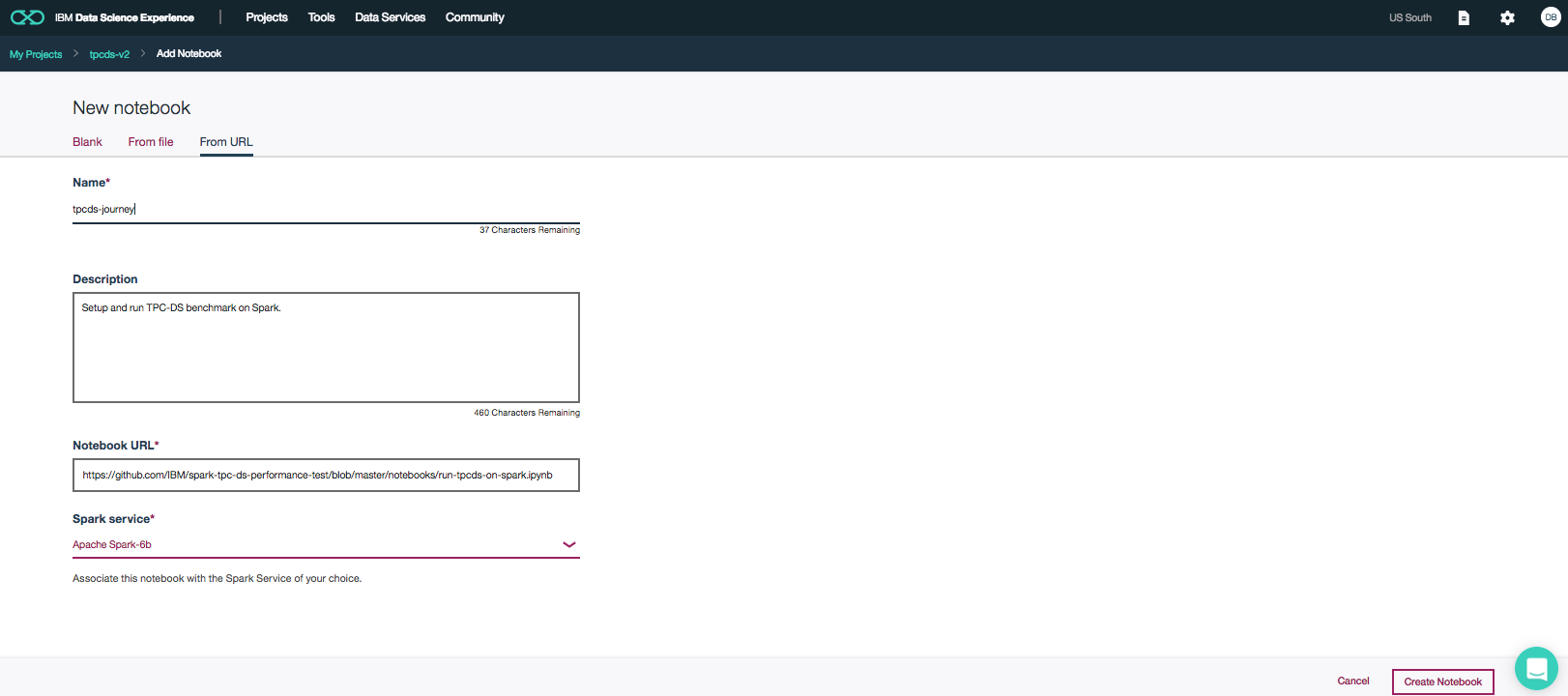
- In Watson Studio, click on
Create notebookto create a notebook. - Create a project if necessary, provisioning an object storage service if required.
- In the
Assetstab, select theCreate notebookoption. - Select the
From URLtab. - Enter a name for the notebook.
- Optionally, enter a description for the notebook.
- Enter this Notebook URL: https://github.com/IBM/spark-tpc-ds-performance-test/blob/master/notebooks/run-tpcds-on-spark.ipynb
- Select the free Anaconda runtime.
- Click the
Createbutton.
3. Run the notebook
When a notebook is executed, what is actually happening is that each code cell in the notebook is executed, in order, from top to bottom.
Each code cell is selectable and is preceded by a tag in the left margin. The tag
format is In [x]:. Depending on the state of the notebook, the x can be:
- A blank, this indicates that the cell has never been executed.
- A number, this number represents the relative order this code step was executed.
- A
*, this indicates that the cell is currently executing.
There are several ways to execute the code cells in your notebook:
- One cell at a time.
- Select the cell, and then press the
Playbutton in the toolbar.
- Select the cell, and then press the
- Batch mode, in sequential order.
- From the
Cellmenu bar, there are several options available. For example, you canRun Allcells in your notebook, or you canRun All Below, that will start executing from the first cell under the currently selected cell, and then continue executing all cells that follow.
- From the
- At a scheduled time.
- Press the
Schedulebutton located in the top right section of your notebook panel. Here you can schedule your notebook to be executed once at some future time, or repeatedly at your specified interval.
- Press the
4. Save and Share
How to save your work:
Under the File menu, there are several ways to save your notebook:
-
Savewill simply save the current state of your notebook, without any version information. -
Save Versionwill save your current state of your notebook with a version tag that contains a date and time stamp. Up to 10 versions of your notebook can be saved, each one retrievable by selecting theRevert To Versionmenu item.
How to share your work:
You can share your notebook by selecting the “Share” button located in the top right section of your notebook panel. The end result of this action will be a URL link that will display a “read-only” version of your notebook. You have several options to specify exactly what you want shared from your notebook:
-
Only text and output: will remove all code cells from the notebook view. -
All content excluding sensitive code cells: will remove any code cells that contain a sensitive tag. For example,# @hidden_cellis used to protect your dashDB credentials from being shared. -
All content, including code: displays the notebook as is. - A variety of
download asoptions are also available in the menu.
Considerations while increasing the scale factor.
This Code Pattern walks us through the steps that need to be performed to run the TPC-DS benchmark with the qualification scale factor(1GB). Since this is a performance benchmark, typically we need to run the benchmark with varying scale factors to gauge the throughput of the underlying data processing engine. In the section below, we will briefly touch on things to be considered while increasing the data and running the workload against a production cluster.
- Generation of the data in larger scale factor: In order to increase the scale, please follow the section titled "Scaling and Database Population" in the benchmark spec.
- Movement of data to the distributed file system: After generating the data, we need to copy or move them to the underlying distributed file system (typically hdfs) that your spark cluster is configured to work with.
- Creation of spark tables: Modify the create table ddl script to change the path to the location of the data after the above copy step. Additionally we may consider to partition the fact tables for better performance.
- We need to tune several spark configs to get optimal performance. Some of them are discussed in the following links.
Learn more
- Data Analytics Code Patterns: Enjoyed this Code Pattern? Check out our other Data Analytics Code Patterns
- AI and Data Code Pattern Playlist: Bookmark our playlist with all of our Code Pattern videos
- Watson Studio: Master the art of data science with IBM's Watson Studio
- Spark on IBM Cloud: Need a Spark cluster? Create up to 30 Spark executors on IBM Cloud with our Spark service
License
This code pattern is licensed under the Apache Software License, Version 2. Separate third party code objects invoked within this code pattern are licensed by their respective providers pursuant to their own separate licenses. Contributions are subject to the Developer Certificate of Origin, Version 1.1 (DCO) and the Apache Software License, Version 2.