TextAugment: Improving Short Text Classification through Global Augmentation Methods
You have just found TextAugment.
TextAugment is a Python 3 library for augmenting text for natural language processing applications. TextAugment stands on the giant shoulders of NLTK, Gensim, and TextBlob and plays nicely with them.
Table of Contents
Features
- Generate synthetic data for improving model performance without manual effort
- Simple, lightweight, easy-to-use library.
- Plug and play to any machine learning frameworks (e.g. PyTorch, TensorFlow, Scikit-learn)
- Support textual data
Citation Paper
Improving short text classification through global augmentation methods.
Requirements
- Python 3
The following software packages are dependencies and will be installed automatically.
$ pip install numpy nltk gensim textblob googletrans
The following code downloads NLTK corpus for wordnet.
nltk.download('wordnet')The following code downloads NLTK tokenizer. This tokenizer divides a text into a list of sentences by using an unsupervised algorithm to build a model for abbreviation words, collocations, and words that start sentences.
nltk.download('punkt')The following code downloads default NLTK part-of-speech tagger model. A part-of-speech tagger processes a sequence of words, and attaches a part of speech tag to each word.
nltk.download('averaged_perceptron_tagger')Use gensim to load a pre-trained word2vec model. Like Google News from Google drive.
import gensim
model = gensim.models.Word2Vec.load_word2vec_format('./GoogleNews-vectors-negative300.bin', binary=True)You can also use gensim to load Facebook's Fasttext English and Multilingual models
import gensim
model = gensim.models.fasttext.load_facebook_model('./cc.en.300.bin.gz')
Or training one from scratch using your data or the following public dataset:
Installation
Install from pip [Recommended]
$ pip install textaugment
or install latest release
$ pip install [email protected]:dsfsi/textaugment.gitInstall from source
$ git clone [email protected]:dsfsi/textaugment.git
$ cd textaugment
$ python setup.py installHow to use
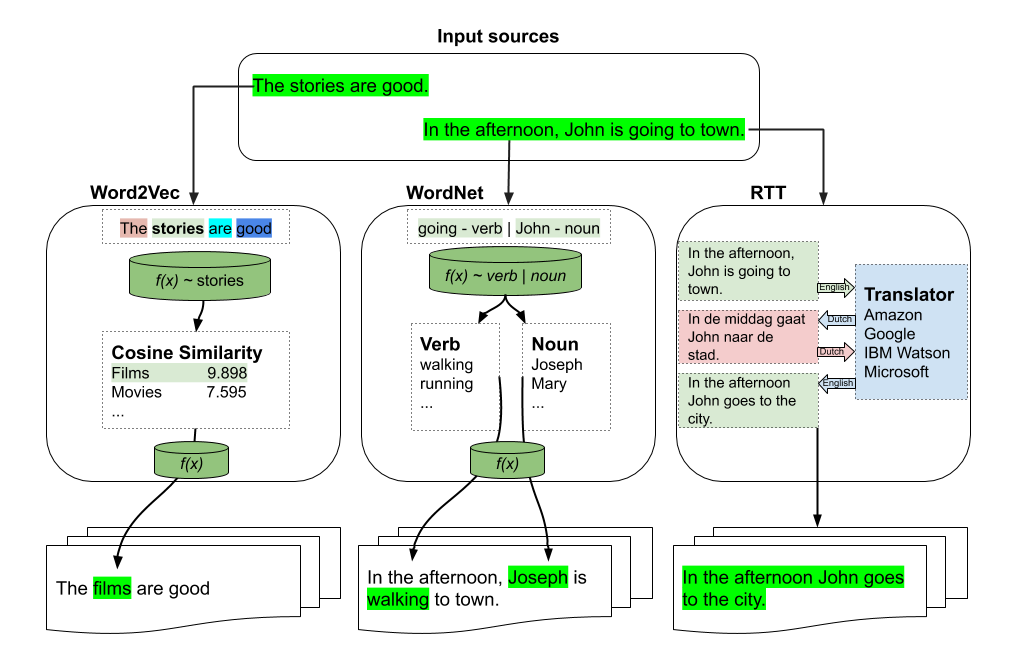
There are three types of augmentations which can be used:
- word2vec
from textaugment import Word2vec- wordnet
from textaugment import Wordnet- translate (This will require internet access)
from textaugment import TranslateWord2vec-based augmentation
See this notebook for an example
Basic example
>>> from textaugment import Word2vec
>>> t = Word2vec(model='path/to/gensim/model'or 'gensim model itself')
>>> t.augment('The stories are good')
The films are goodAdvanced example
>>> runs = 1 # By default.
>>> v = False # verbose mode to replace all the words. If enabled runs is not effective. Used in this paper (https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~diyiy/docs/emnlp_wang_2015.pdf)
>>> p = 0.5 # The probability of success of an individual trial. (0.1<p<1.0), default is 0.5. Used by Geometric distribution to selects words from a sentence.
>>> t = Word2vec(model='path/to/gensim/model'or'gensim model itself', runs=5, v=False, p=0.5)
>>> t.augment('The stories are good')
The movies are excellentWordNet-based augmentation
Basic example
>>> import nltk
>>> nltk.download('punkt')
>>> nltk.download('wordnet')
>>> from textaugment import Wordnet
>>> t = Wordnet()
>>> t.augment('In the afternoon, John is going to town')
In the afternoon, John is walking to townAdvanced example
>>> v = True # enable verbs augmentation. By default is True.
>>> n = False # enable nouns augmentation. By default is False.
>>> runs = 1 # number of times to augment a sentence. By default is 1.
>>> p = 0.5 # The probability of success of an individual trial. (0.1<p<1.0), default is 0.5. Used by Geometric distribution to selects words from a sentence.
>>> t = Wordnet(v=False ,n=True, p=0.5)
>>> t.augment('In the afternoon, John is going to town')
In the afternoon, Joseph is going to town.RTT-based augmentation
Example
>>> src = "en" # source language of the sentence
>>> to = "fr" # target language
>>> from textaugment import Translate
>>> t = Translate(src="en", to="fr")
>>> t.augment('In the afternoon, John is going to town')
In the afternoon John goes to townEDA: Easy data augmentation techniques for boosting performance on text classification tasks
This is the implementation of EDA by Jason Wei and Kai Zou.
https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/D19-1670.pdf
See this notebook for an example
Synonym Replacement
Randomly choose n words from the sentence that are not stop words. Replace each of these words with one of its synonyms chosen at random.
Basic example
>>> from textaugment import EDA
>>> t = EDA()
>>> t.synonym_replacement("John is going to town")
John is give out to townRandom Deletion
Randomly remove each word in the sentence with probability p.
Basic example
>>> from textaugment import EDA
>>> t = EDA()
>>> t.random_deletion("John is going to town", p=0.2)
is going to townRandom Swap
Randomly choose two words in the sentence and swap their positions. Do this n times.
Basic example
>>> from textaugment import EDA
>>> t = EDA()
>>> t.random_swap("John is going to town")
John town going to isRandom Insertion
Find a random synonym of a random word in the sentence that is not a stop word. Insert that synonym into a random position in the sentence. Do this n times
Basic example
>>> from textaugment import EDA
>>> t = EDA()
>>> t.random_insertion("John is going to town")
John is going to make up townMixup augmentation
This is the implementation of mixup augmentation by Hongyi Zhang, Moustapha Cisse, Yann Dauphin, David Lopez-Paz adapted to NLP.
Used in Augmenting Data with Mixup for Sentence Classification: An Empirical Study.
Mixup is a generic and straightforward data augmentation principle. In essence, mixup trains a neural network on convex combinations of pairs of examples and their labels. By doing so, mixup regularises the neural network to favour simple linear behaviour in-between training examples.
Implementation
See this notebook for an example
Built with ❤ on
Authors
Acknowledgements
Cite this paper when using this library. Arxiv Version
@inproceedings{marivate2020improving,
title={Improving short text classification through global augmentation methods},
author={Marivate, Vukosi and Sefara, Tshephisho},
booktitle={International Cross-Domain Conference for Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction},
pages={385--399},
year={2020},
organization={Springer}
}
Licence
MIT licensed. See the bundled LICENCE file for more details.