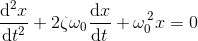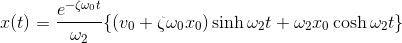skevy / Wobble
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Wobble
A tiny (~1.7 KB gzipped) spring physics micro-library that models a damped harmonic oscillator.
Why Would I Use This?
Perhaps, you just really like to dance.
Use wobble if you need a very small and accurate damped harmonic spring simulation in your animation library or application. wobble intentionally only provides a way to animate a scalar value according to equations governing damped harmonic motion. That's all this library will ever do -- any other functionality (integration with [insert ui library here], multi-dimensional springs, a nice API around chaining springs together, etc.) is left to the reader to implement.
Background
Using spring physics in UI design is a common way to express natural motion, and there are several ways to model the physics behind springs.
There are two main ways that spring physics is typically implemented: numerical integration (using something like the Runge-Kutta 4th order numerical integration method) or by using a closed-form (exact) solution. Numerical integration is an approximation of the exact solution, and is generally easier to derive. The numerical integration technique can be applied to basically any ordinary differential equation. Though there are several different numerical integration methods, it's common to leverage RK4 when accuracy of the approximation is required, even though it's slightly slower. RK4 is commonly used in other animation libraries, such as Rebound and Pop.
The original goal of the algorithm used in wobble was to replicate CASpringAnimation from Apple's Core Animation library (used to power animations on macOS and iOS) in order to mimic iOS animations in React Native. After doing a little spelunking inside QuartzCore.framework, it became clear that Apple was using the closed-form solution for damped harmonic oscillation to power CASpringAnimation. wobble leverages the same equations as CASpringAnimation in order to be able to match Apple animations precisely.
The closed-form solution lets us calculate position (x) and velocity (v) from time t, and thus it turns out that using the closed-form solution provides a couple advantages over RK4:
- Easier to generate keyframes and build continuous/interruptible gestures and animations, due to the fact that x and v are pure functions of t.
- Less code.
- It's faster.
Math!
The ODE for damped harmonic motion is:
Solving this ODE yields:
And from this general solution, we're able to easily derive the solutions for under-damped, critically-damped, and over-damped damped harmonic oscillation.
The full proof can be found in this PDF from planetmath.org.
Demos
Wobble demos are located here: https://wobble-demos.now.sh/. Send PRs to add more!
... and of course, Our FAVORITE Demo
Getting Started
yarn add wobble
# or
npm install --save wobble
Usage
import { Spring } from 'wobble';
// Create a new spring
const spring = new Spring({
toValue: 100,
stiffness: 1000,
damping: 500,
mass: 3,
});
// Set listeners for spring events, start the spring.
spring
.onStart(() => {
console.log('Spring started!');
})
.onUpdate((s) => {
console.log(`Spring's current value: ` + s.currentValue);
console.log(`Spring's current velocity: ` + s.currentVelocity);
})
.onStop(() => {
console.log('Spring is at rest!');
})
.start();
API
new Spring(config: SpringConfig)
Initialize a new spring with a given spring configuration.
Configuration
fromValue: number
Starting value of the animation. Defaults to 0.
toValue: number
Ending value of the animation. Defaults to 1.
stiffness: number
The spring stiffness coefficient. Defaults to 100.
damping: number
Defines how the spring’s motion should be damped due to the forces of friction. Defaults to 10.
mass: number
The mass of the object attached to the end of the spring. Defaults to 1.
initialVelocity: number
The initial velocity (in units/ms) of the object attached to the spring. Defaults to 0.
allowsOverdamping: boolean
Whether or not the spring allows "overdamping" (a damping ratio > 1). Defaults to false.
overshootClamping: boolean
False when overshooting is allowed, true when it is not. Defaults to false.
restVelocityThreshold: number
When spring's velocity is below restVelocityThreshold, it is at rest. Defaults to .001.
restDisplacementThreshold: number
When the spring's displacement (current value) is below restDisplacementThreshold, it is at rest. Defaults to .001.
Methods
start(): Spring
If fromValue differs from toValue, or initialVelocity is non-zero, start the simulation and call the onStart listeners.
stop(): Spring
If a simulation is in progress, stop it and call the onStop listeners.
updateConfig(updatedConfig: PartialSpringConfig): Spring
Updates the spring config with the given values. Values not explicitly supplied will be reused from the existing config.
onStart(listener: SpringListenerFn): Spring
The provided callback will be invoked when the simulation begins.
onUpdate(listener: SpringListenerFn): Spring
The provided callback will be invoked on each frame while the simulation is running.
onStop(listener: SpringListenerFn): Spring
The provided callback will be invoked when the simulation ends.
removeListener(listenerFn: SpringListenerFn): Spring
Remove a single listener from this spring.
removeAllListeners(): Spring
Removes all listeners from this spring.
Properties
currentValue: number
The spring's current displacement.
currentVelocity: number
The spring's current velocity in units / ms.
isAtRest: boolean
If the spring has reached its toValue, or if its velocity is below the restVelocityThreshold, it is considered at rest. If stop() is called during a simulation, both isAnimating and isAtRest will be false.
isAnimating: boolean
Whether or not the spring is currently emitting values. Note: this is distinct from whether or not it is at rest. See also isAtRest.
Credits
Brenton Simpson (@appsforartists) - For his assistance in creating and testing this library.
Devine Lu Linvega (@neauoire) - The awesome logo!