ZigZagBoomerang
Overview
Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods are used to sample from a probability distribution, for example the posterior distribution in a Bayesian model. Piecewise deterministic Monte Carlo (PDMC) methods which are implemented in ZigZagBoomerang.jl have the same goal except for the fact that here the distribution is explored through the continuous movement of a particle and not one point at a time.
Here, the particle changes direction at random times and moves otherwise on deterministic trajectories (for example along a line with constant velocity, see the picture)
The random direction changes are calibrated such that the trajectory of the particle samples the right distribution; from the trajectory, the quantities of interest, such as the posterior mean and standard deviation, can be estimated.
The decision of whether to change direction only requires the evaluation of a partial derivatives which depend on few coordinates -- the neighbourhood of the coordinate in the Markov blanket. That allows exploiting multiple processor cores using Julia's multithreaded parallelism (or other forms of parallel computing).
Joris Bierken's Overview over Piecewise Deterministic Monte Carlo together with our announcement on Discourse [ANN] ZigZagBoomerang.jl is a good starting point for the theory and applications of the methods covered in ZigZagBoomerang.jl.
Features
Subsampling. One highlight is that these samplers do not introduce error by allowing subsampling of data. This is because they just need an unbiased estimate of the gradient of the log densities to sample from a target distribution. [1]
The factorised samplers make use of a sparse Gaussian approximation of the target density (in form of a sparse precision matrix Γ).
Local factorised samplers. ZigZag and the factorised Boomerang can optionally make use of the sparsity of the gradient of the log density, see spdmp. [3]
Sticky samplers. A recent feature is the addition of sticky PDMPs for variable selection (order 10000s of variables for well structured problems.), see sspdmp. [4]
Multithreaded Zig-Zag. We are currently developing a multi-threaded version of the local Zig-Zag.
Probabilistic programming with PDMPs. One challenge with PDMPs is their less familiar theory compared to Markov chains. We strive to provide a ready-to-use sampler suitable as backend for other packages with the aim of making PDMP methods more accecible for users.
Contents
The package provides efficient and modular implementations of samplers of several piecewise deterministic Markov processes (PDMP), the Bouncy Particle, the Boomerang, the ZigZag, and the factorised Boomerang and their sticky versions.
The sampler requires the gradient of the potential of the target density as input and are called through pdmp producing a trajectory. pdmp_inner! gives access to the transition function of the sampler.
The non-factorised samplers (Bouncy Particle, the Boomerang)
take a function ∇ϕ!(y, x) writing the gradient of the potential ϕ(x) = -log(p(x)) of the target density p into y. The factorised samplers (factorised Boomerang and ZigZag) take ∇ϕ(x, i), the i's partial derivative of ϕ (that is y[i].)
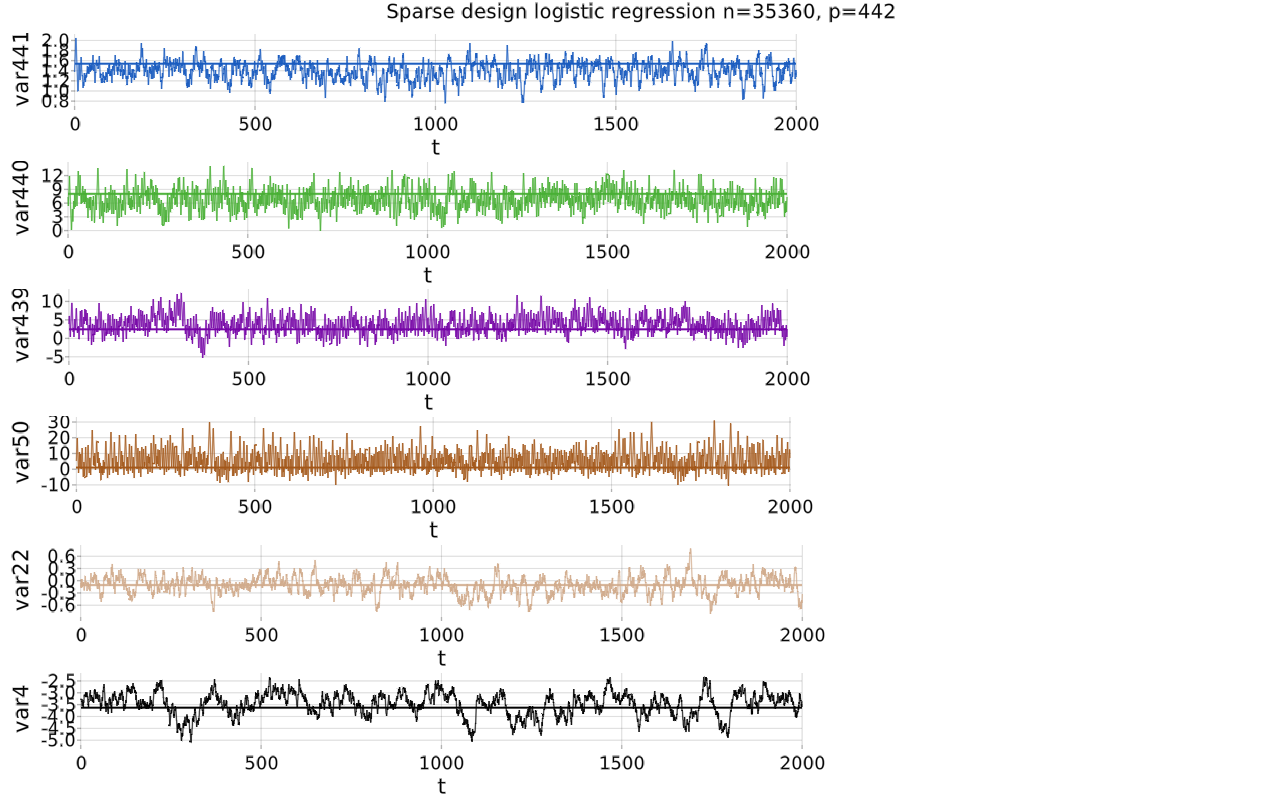
See [https://github.com/mschauer/ZigZagBoomerang.jl/tree/master/scripts/logistic.jl] for a worked out example (logistic regression with n=8840, p=442 and sparse Gramian) sampling from a non-Gaussian target with structured sparse gradient of the potential and unbiased estimate of the gradient subsampling of the n observations.
JuliaCon 2021
Gallery
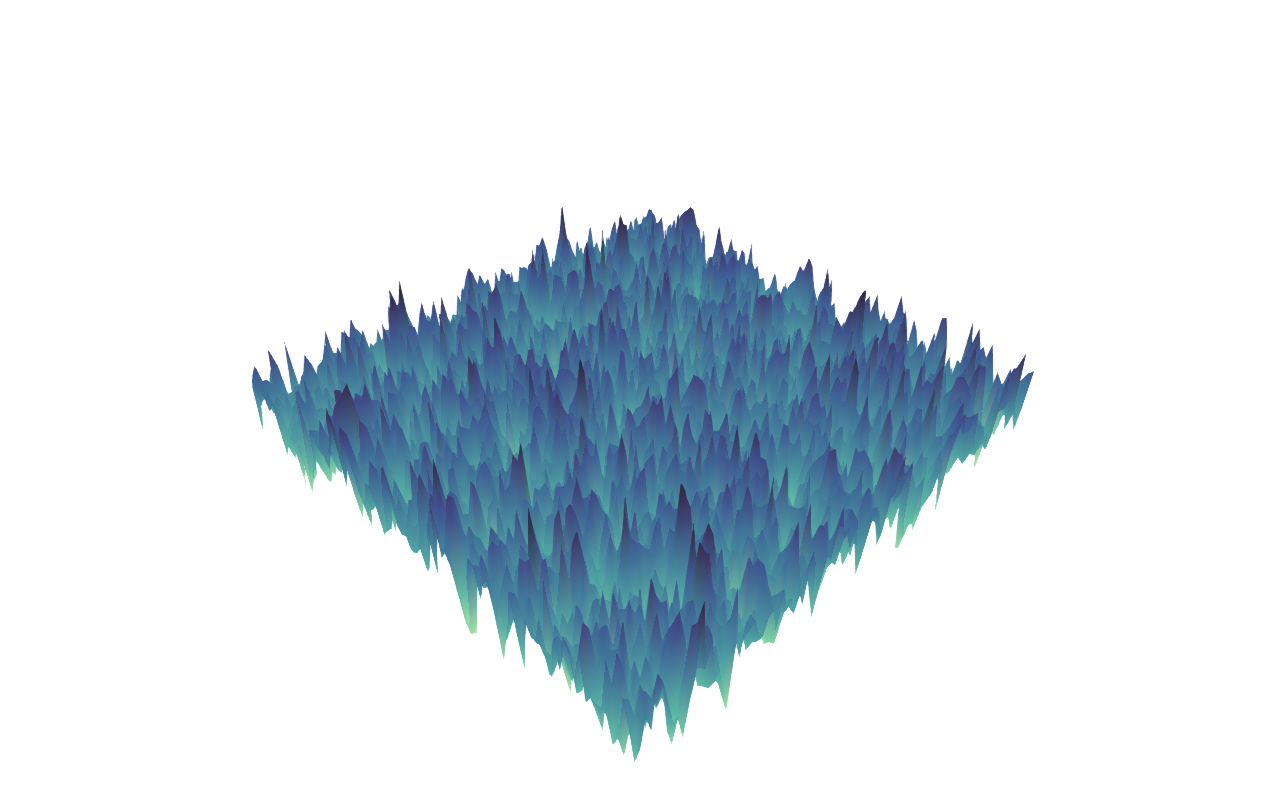
Showing mixing and convergence from white noise to a Gaussian random field: ZigZag after 10, after 30, after 50 time units. See the script folder for the example and a video.
Examples
See [https://github.com/mschauer/ZigZagBoomerang.jl/tree/master/scripts].
Literature
- Joris Bierkens, Paul Fearnhead, Gareth Roberts: The Zig-Zag Process and Super-Efficient Sampling for Bayesian Analysis of Big Data. The Annals of Statistics, 2019, 47. Vol., Nr. 3, pp. 1288-1320. [https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.03188].
- Joris Bierkens, Sebastiano Grazzi, Kengo Kamatani and Gareth Robers: The Boomerang Sampler. ICML 2020. [https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13777].
- Joris Bierkens, Sebastiano Grazzi, Frank van der Meulen, Moritz Schauer: A piecewise deterministic Monte Carlo method for diffusion bridges. Statistics and Computing, 2021 (to appear). [https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.05889].
- Joris Bierkens, Sebastiano Grazzi, Frank van der Meulen, Moritz Schauer: Sticky PDMP samplers for sparse and local inference problems. 2020. [https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.08478].
- Joris Bierkens, Alexandre Bouchard-Côté, Arnaud Doucet, Andrew B. Duncan, Paul Fearnhead, Thibaut Lienart, Gareth Roberts, Sebastian J. Vollmer: Piecewise deterministic Markov processes for scalable Monte Carlo on restricted domains, Statistics & Probability Letters, 136. 2018. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spl.2018.02.021].
- Joris Bierkens, Andrea Bertazzi: Adaptive Schemes for Piecewise Deterministic Monte Carlo Algorithms, 2020. [https://arxiv.org/abs/arXiv:2012.13924].
- Werner Krauth: Event-chain Monte Carlo: foundations, applications, and prospects, 2021. [https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.07217].
- [https://github.com/jbierkens/ICML-boomerang/] (code accompanying the paper "The Boomerang Sampler")