py-bin / Dianping_textmining
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Dianping textmining
大众点评评论文本挖掘
[TOC]
一、爬虫
整体思路
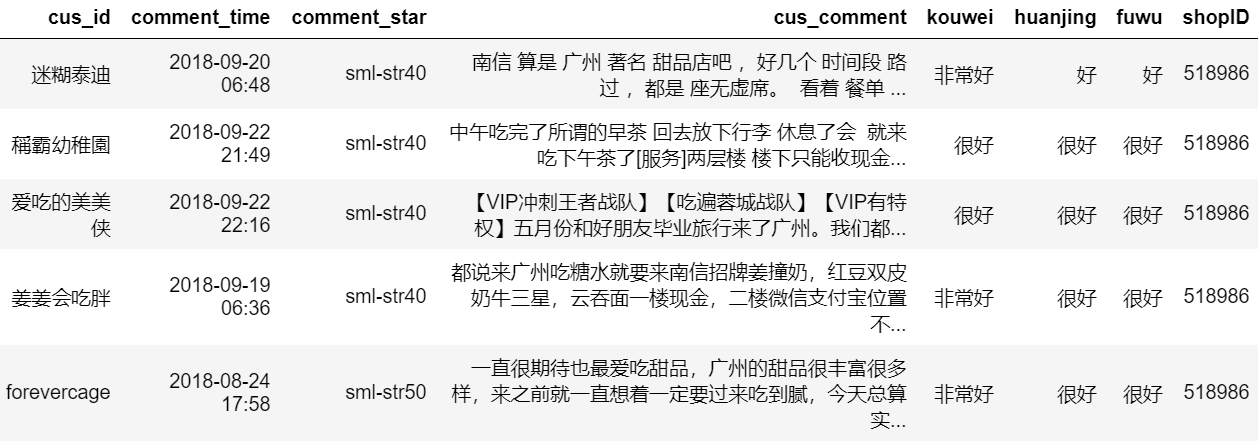
爬取大众点评十大热门糖水店的评论,爬取网页后从html页面中把需要的字段信息(顾客id、评论时间、评分、评论内容、口味、环境、服务、店铺ID)提取出来并存储到MYSQL数据库中。
网页爬取和解析
链接格式为"http://www.dianping.com/shop/" + shopID + "/review_all/" + pi,如:http://www.dianping.com/shop/518986/review_all/p1 ,一页评论有20条。我们使用for循环构造链接URL,使用requests库发起请求并把html页面爬取下来,通过BeautifulSoup和re库解析页面提取信息。
我们发现完整的评论都存储在'div','main-review'中,且部分页面口味、环境、服务并不是每一页都有,因此需要使用try...except...防止程序中断,BeautifulSoup部分代码如下:
for item in soup('div','main-review'):
cus_id = item.find('a','name').text.strip()
comment_time = item.find('span','time').text.strip()
comment_star = item.find('span',re.compile('sml-rank-stars')).get('class')[1]
cus_comment = item.find('div',"review-words").text.strip()
scores = str(item.find('span','score'))
try:
kouwei = re.findall(r'口味:([\u4e00-\u9fa5]*)',scores)[0]
huanjing = re.findall(r'环境:([\u4e00-\u9fa5]*)',scores)[0]
fuwu = re.findall(r'服务:([\u4e00-\u9fa5]*)',scores)[0]
except:
kouwei = huanjing = fuwu = '无'
数据存储
我们使用MYSQL数据库,安装教程参考菜鸟教程,python连接MYSQL数据推荐使用pymysql,同样是推荐菜鸟教程菜鸟教程。我们需要先建立一个数据库和表,然后连接并定义游标,然后写对应的sql语句,最后执行事务,存储部分的代码如下:
#连接MYSQL数据库
db = pymysql.connect("localhost","root","","TESTDB" )
cursor = db.cursor()
#存储爬取到的数据
def save_data(data_dict):
sql = '''INSERT INTO DZDP(cus_id, comment_time, comment_star, cus_comment, kouwei, huanjing, fuwu, shopID) VALUES(%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s)'''
value_tup = (data_dict['cus_id']
,data_dict['comment_time']
,data_dict['comment_star']
,data_dict['cus_comment']
,data_dict['kouwei']
,data_dict['huanjing']
,data_dict['fuwu']
,data_dict['shopID']
)
try:
cursor.execute(sql,value_tup)
db.commit()
except:
print('数据库写入失败')
return
反爬虫对抗
-
修改请求头中浏览器信息:使用fake_useragent第三方库,修改request中的headers参数,用法如下:
from fake_useragent import UserAgent ua = UserAgent() headers = {'User-Agent':ua.random}
-
设置跳转路径:在访问评论时,一般的浏览行为是从某一页跳转到下一页这样的,而不是直接通过连接访问,为了更好的伪装成一个正常的访问,我们需要设置一下跳转的路径,修改headers中的Referer参数
headers = { 'User-Agent':ua.random, 'Cookie':cookie, 'Referer': 'http://www.dianping.com/shop/518986/review_all' }
-
设置Cookies:评论数据需要登录后才能获取,下面介绍一种非常简单方便的绕过登录的方法。
- 在网页上进行登录
- 使用Chrome浏览器的开发者工具,查询当前请求的cookie
- 复制浏览器中的cookie,使用此cookie对我们的请求进行伪装
-
使用IP代理池:这里使用西刺代理的免费代理,构建一个爬虫爬取西刺代理的ip,然后进行验证,筛掉不可用的ip,构建出ip池供后续调用,代码来自网络。但是经过测试,大众点评对一个账号不同ip访问监控非常严格,使用IP代理池不更换账号的话,死的更快,封你账号,然而构建账号池比较麻烦,我们先暂缓。
-
降低爬取频率:一个简单又有效的方法就是降低爬取频率,毕竟高频率的爬取对服务器也是一个考验,如果对速度的要求不是很高的话,建议把频率放慢一点,你好我好大家好!
import random import time time.sleep(6*random.random() + 4)
-
设置断点续传:即使降低了爬取频率,有时还是会被美团的网络工程师抓到的,小哥哥饶命啊~。因此我们需要一个断点续传的小功能,避免每次都从头开始爬。思路是建一个文本文件,存储当前爬取的进度,每次运行程序时都出当前进度开始,详见代码~
二、探索性分析与文本数据预处理
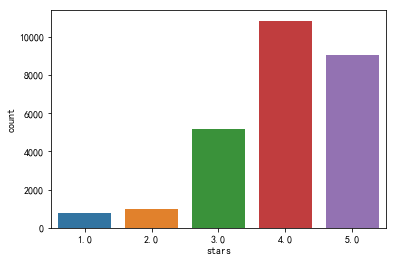
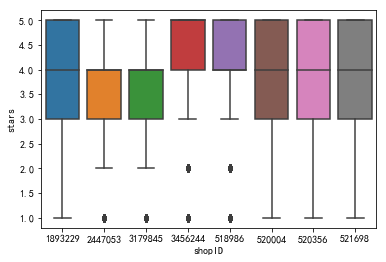
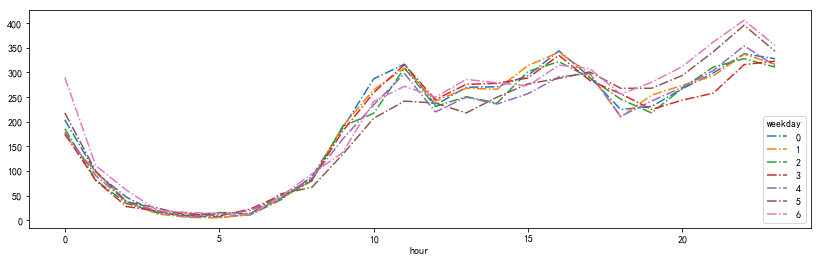
探索性分析
数据预处理
-
去除非文本数据:可以看出,爬虫获取的数据非常多类似“\xa0”的非文本数据,而且都还有一些无意义的干扰数据,如结尾的“收起评论”
#除去非文本数据和无意义文本 data['cus_comment'] = data['cus_comment'].str.replace(r'[^\u4e00-\u9fa5]','').str.replace('收起评论','')
-
中文分词:中文文本数据处理,怎么能离开中文分词呢,我们使用jieba库,简单又好用。这里我们把文本字符串处理为以空格区隔的分词字符串
#中文分词 import jieba data['cus_comment'] = data['cus_comment'].apply(lambda x:' '.join(jieba.cut(x)))
-
去除停用词:文本中有很多无效的词,比如“着”,“和”,还有一些标点符号,这些我们不想在文本分析的时候引入,因此需要去掉,因为wordcloud和TF-IDF都支持停用词,因此就不额外处理了
词云展示
三、文本的情感分析
先上结果:
| 糖水店的评论文本 | 模型预测的情感评分 |
|---|---|
| '糖水味道不错,滑而不腻,赞一个,下次还会来' | 0.91 |
| '味道一般,没啥特点' | 0.52 |
| '排队老半天,环境很差,味道一般般' | 0.05 |
模型的效果还可以的样子,yeah~接下来我们好好讲讲怎么做的哈,我们通过爬虫爬取了大众点评广州8家最热门糖水店的3W条评论信息以及评分作为训练数据,前面的分析我们得知样本很不均衡。接下来我们的整体思路就是:文本特征提取(TF-IDF)—机器学习建模—模型评价。
我们先不处理样本不均衡问题,直接建模后查看结果,接下来我们再按照两种方法处理样本不均衡,对比结果。
文本特征提取(TF-IDF)
模型不能直接处理文本数据,因此需要先把文本数据转为向量,方法有词库表示法、TF-IDF、word2vec等,推荐一篇文章,总结得不错 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/44917421。
#使用TF-IDF进行文本转向量处理
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
tv = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=stopwords, max_features=3000, ngram_range=(1,2))
tv.fit(x_train)
机器学习建模
这里我们使用文本分类的经典算法朴素贝叶斯算法,而且朴素贝叶斯算法的计算量较少。特征值是评论文本经过TF-IDF处理的向量,标签值评论的分类共两类,好评是1,差评是0。情感评分为分类器预测分类1的概率值。
#计算分类效果的准确率
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, f1_score
classifier = MultinomialNB()
classifier.fit(tv.transform(x_train), y_train)
classifier.score(tv.transform(x_test), y_test)
>>>0.9275308869629356
可以看出,准确率非常不错的样子
#从大众点评网找两条评论来测试一下
test1 = '很好吃,环境好,所有员工的态度都很好,上菜快,服务也很好,味道好吃,都是用蒸馏水煮的,推荐,超好吃' #5星好评
test2 = '糯米外皮不绵滑,豆沙馅粗躁,没有香甜味。12元一碗不值。' #1星差评
print('好评实例的模型预测情感得分为{}\n差评实例的模型预测情感得分为{}'.format(ceshi(classifier,test1),ceshi(classifier,test2)))
>>>好评实例的模型预测情感得分为0.8638082706675478
>>>差评实例的模型预测情感得分为0.7856544482460911
点评网上的实际测试中,5星好评模型预测出来了,1星差评缺预测错误。为什么呢?我们查看一下混淆矩阵
[ 46, 385]
[ 8, 4984]
可以看出,负类的预测非常不准,433单准确预测为负类的只有15.7%,应该是由于数据不平衡导致的,模型的默认阈值为输出值的中位数。比如逻辑回归的输出范围为[0,1],当某个样本的输出大于0.5就会被划分为正例,反之为反例。在数据的类别不平衡时,采用默认的分类阈值可能会导致输出全部为正例,产生虚假的高准确度,导致分类失败。
处理样本不均衡问题的方法,首先可以选择调整阈值,使得模型对于较少的类别更为敏感,或者选择合适的评估标准,比如ROC或者F1,而不是准确度(accuracy)。另外一种方法就是通过采样(sampling)来调整数据的不平衡。其中欠采样抛弃了大部分正例数据,从而弱化了其影响,可能会造成偏差很大的模型,同时,数据总是宝贵的,抛弃数据是很奢侈的。另外一种是过采样,下面我们就使用过采样方法来调整。
样本数据不平衡
最简单的过采样方法,就是简单复制法。但单纯的重复了反例,会过分强调已有的反例。如果其中部分点标记错误或者是噪音,那么错误也容易被成倍的放大。因此最大的风险就是对反例过拟合。
#把0类样本复制10次,构造训练集
index_tmp = y_train==0
y_tmp = y_train[index_tmp]
x_tmp = x_train[index_tmp]
x_train2 = pd.concat([x_train,x_tmp,x_tmp,x_tmp,x_tmp,x_tmp,x_tmp,x_tmp,x_tmp,x_tmp,x_tmp])
y_train2 = pd.concat([y_train,y_tmp,y_tmp,y_tmp,y_tmp,y_tmp,y_tmp,y_tmp,y_tmp,y_tmp,y_tmp])
#使用过采样样本(简单复制)进行模型训练,并查看准确率
clf2 = MultinomialNB()
clf2.fit(tv.transform(x_train2), y_train2)
y_pred2 = clf2.predict_proba(tv.transform(x_test))[:,1]
roc_auc_score(y_test,y_pred2)
>>>0.9049699937533463
查看此时的混淆矩阵
[ 331, 100]
[ 637, 4355]
可以看出,即使是简单粗暴的复制样本来处理样本不平衡问题,负样本的识别率大幅上升了,变为77%,满满的幸福感呀。还有SMOTE过采样算法,SMOTE是在局部区域通过K-近邻生成了新的反例。相较于简单的过采样,SMOTE降低了过拟合风险,但同时运算开销加大,详细请看具体代码~
模型评估测试
我们把3W条数据都拿来训练,数据量变多了,模型效果应该会更好
def fenxi(strings):
strings_fenci = fenci(pd.Series([strings]))
return float(clf.predict_proba(tv2.transform(strings_fenci))[:,1])
#到网上找一条差评来测试一下
fenxi('糯米外皮不绵滑,豆沙馅粗躁,没有香甜味。12元一碗不值。')
>>>0.28900092243477077
只用到了简单的机器学习,就做出了不错的情感分析效果,知识的力量真是强大呀,666~
四、拓展应用及后续方向
- 使用更复杂的机器学习模型如神经网络、支持向量机等
- 模型的调参
- 行业词库的构建
- 增加数据量
- 优化情感分析的算法
- 增加标签提取等
- 项目部署到服务器上,更好地分享和测试模型的效果