Drowsiness driving detection system with OpenCV & KNN
: In this repository, a program was developed to identify the driver's drowsiness based on real-time camera image and image processing techniques, and this program makes warning alarms go off for each level of drowsiness when it detects drowsiness driving.
: 실시간 영상과 영상 처리 기술을 기반으로 운전자의 졸음 상태를 판별하고 졸음운전 중이라면 특정 수준에 따라 경고 알람이 울리게 하는 프로그램을 제작하였습니다. 실시간 Vision System에 운전자의 얼굴 및 안구 검출 기법, 조명 영향 제거에 따른 안구 오검출 제거 방법, 졸음 감지 기법, 지도 학습 알고리즘을 사용한 졸음 단계 판별법 등을 구현하였습니다.
Description
: Based on the real-time Vision System, drivers' face and eye detection techniques were added, as well as removing lighting effects due to the eye detection false positives, drowsiness detection techniques, and supervised learning algorithms to identify drowsiness level.
The Histogram of Oriented Gradients technology and the learned Face Landmark estimation techniques were used to detect faces and eyes.
In order to eliminate the effects of lighting, the light channels of the original images were separated and reversed, and then composed with the grayscale images of original images.
Furthermore the concept of Eye Aspect Ratio was used to detect drivers' drowsiness.
Finally, the KNN algorithm was used to divide the drivers' level of drowsiness into three stages, and differential alarms go off for each stages.
Through these works, we could research and make technology of intelligent vehicle systems and vision computing, which is gaining much attention recently.
: 얼굴 및 안구 검출을 하기 위해 Histogram of Oriented Gradients 기술과 학습된 Face landmark estimation 기법을 사용하였습니다. 조명 영향을 제거하기 위해선 원본 영상의 조명 채널을 분리해 역 조명을 쏘아 Grayscale 된 이미지와 합쳐주었고, 졸음 상태를 감지하기 위해선 Eye Aspect Ratio라는 개념을 사용하였습니다. 마지막으로 운전자의 졸음 위험 수준을 세 단계로 나눠 단계별로 차등 알람이 울리게 하였고, 단계를 나누는 과정에서 KNN 알고리즘을 사용했다.
This code is in Python 3.6
System diagram
Get face images from the camera -> Grayscaling -> Light processing -> HOG & find face -> Face Landmark Estimation -> Detect drowsiness driving.
- In detail
0 : The filming.
10 : Lightness preprocessing.
100 : Detecting drowsiness.
110 : Getting face's image.
120 : Finding eyes region.
130 : Determining the value of the EAR normally.
140 : Determining drowsiness driving.
141 : Calculating the value of the EAR.
142 : Calculating the amount of time eyes are closed.
143 : Calculating the amount of time eyes are opened.
144 : Determining the level of the drowsiness.
Extracting face and eye region
- Using the HOG face pattern, to find the face from the Grayscaled-HOG-input-image.
- 그레이스케일링 한 이미지에서 얼굴을 찾기 위해 HOG face pattern을 사용했습니다.
- Use the Face Landmark Estimation algorithm to locate the landmarks on the face.
- Face Landmark Estimation 알고리즘을 사용해 얼굴의 68개 랜드마크를 찾아냈습니다.
Preprocessing
- Invert the lightness channel detached from the original image and composed it with the original grayscale image to produce a clear image.
- 영상에 있어서 조명의 영향은 영상처리에 상당히 많은 영향을 끼칩니다. 특히 그라데이션 조명을 받았을 경우 에러를 일으키는 요소가 되기 때문에, 전처리 과정으로 영상에서 조명 영향을 받을 때 그 영향을 최소화하는 작업을 진행했습니다.
- 전처리를 위해 영상에서 분리한 Lightness 채널을 반전시키고 Grayscale 된 원본 영상과 합성하여 Clear 한 Image를 만들었습니다.
- Converting color to grayscale using Luma Coding
- 그레이스케일링 과정은 Luma 기법을 사용했습니다.
- There are many different models in Color Space, the LAB color space model is the best way to separate Lightness. Median filtering is applied to convert the value of lightness(L) obtained by using the LAB color space to match the actual lighting conditions because it differs from the actual lighting conditions.
- The pictures below are the original image, image that separates L channel, image with Median filter applied, and inverted images from left to right. Drowsiness detection method
- Color Space 모델에는 다양한 모델이 있는데 그중 LAB 모델은 Lightness를 가장 잘 분리해 낼 수 있는 모델입니다.
- LAB 컬러 공간을 사용해 얻게 된 명도 값은 실제 조명의 상태와는 차이가 있기 때문에 실제 조명의 상태에 맞게 변환하고자 메디안 필터링(Median Filtering)을 적용하는 과정을 진행했고, 이렇게 검출된 조명에 역상을 취하여 원 이미지와 합성함으로써 조명의 영향을 줄였습니다.
- 아래의 사진은 왼쪽부터 순서대로 원본 이미지, L 채널을 분리한 이미지, Median Filter를 적용한 이미지, Invert 된 이미지입니다.
- Results of preprocessing
Drowsiness detection method
- Each eye is represented by 6 (x, y)-coordinates
- 이 프로젝트에서는 2016년 Tereza Soukupova & Jan ´ Cech에 의해 제시된 Eyes Aspect Ratio(이하 EAR) 방식을 사용합니다. EAR은 검출된 안구에 여섯 개의 (x, y) 좌표를 이용하여 계산됩니다.
- The EAR equation
- Calculated EAR
- The calculated EAR will have a value more than zero when the eyes are open, and a value close to zero when the eyes are closed.
- This program has set a 50% value from the average EAR value to the threshold value. So, 1) measures the average EAR value when the eyes are open, 2) measures the average EAR value when the driver is closing his eyes, and 3) sets the threshold using the above two results.
- .1) == 과정 1), 2) == 과정 2), 3) == 과정 3) (in drowsiness_detector code)
- 계산된 EAR은 눈을 뜨고 있을 땐 0이 아닌 어떤 값을 갖게 되고, 눈을 감을 땐 0에 가까운 값을 갖습니다. 여기에 어떤 Constant로 Threshold를(졸음운전을 판단할 때 사용하는 임곗값) 설정할 시 그 값보다 EAR 값이 작아지는지 확인하는 방식으로 운전자가 졸음운전 중이라는 것을 감지할 수 있습니다.
- 추가로 졸음운전 판별 시 양쪽 눈을 따로 검사할 필요는 없기 때문에 양쪽 눈 각각의 EAR 값을 평균 계산해서 사용하였습니다.
- Threshold 값은 눈을 가장 크게 떴을 때 EAR 값의 50%로 설정했습니다. 이보다 작을 때는(눈 크기가 작아졌을 때) 운전자가 졸린 상태인 것으로 판단, 운전자가 졸려 하는지에 관심을 뒀기 때문에 완전 수면에 빠지지 않더라도 알람이 울립니다.
- 이 알고리즘을 적용하기 위해 다음의 세 과정을 적용했습니다. 1) 운전자가 눈을 뜨고 있을 때 평균 EAR 값을 결정, 2) 운전자가 눈을 감고 있을 때 평균 EAR 값을 결정, 3) 위의 두 값을 이용해 눈을 뜨고 있는 상태의 50%가 되는 EAR 값을 결정.
Drowsiness level selection
- Conditions :
- 30 FPS
- Prescribed speed : 100km/h, Retention distance between vehicles >= 100m
- The time which takes a person to push the brakes 0.45 (response time) + 0.2 (brake pushing time) + 0.05 (time to start braking) = 0.7 seconds
- The braking distance of a vehicle running at 100 km/h is 56 meters (the driver has 44 meters of free distance)
- Under the above conditions, the drivers has almost 0.9 seconds of free time (100km/h -> 27m/s == 1.63s of free time. 1.63 - 0.7 = 0.9 s).
- 30 FPS -> 27 frame = 0.9s.
- if EAR < threshold for 27 frame? then going alarm off.
- Now I separated the drowsiness phase into three steps.
- 위의 조건을 토대로 다음과 같이 계산할 수 있습니다. "100km/h로 달리는 차량이 앞차와 안전거리를 유지하고 있다고 가정할 시 정지 상태의 장애물과 충돌하지 않기 위해선 56m의 제동 구간이 필요하다. 즉, 운전자에겐 44m 정도의 여유 거리가 있는 것이다. 100km/h는 1초에 27m를 이동한다. 따라서 운전자에겐 1.63초의 여유 시간이 있다. 이 시간에서 브레이크를 밟는데 걸리는 반응 속도를 빼면 약 0.9초의 시간이 남는다."
- 결론적으로 졸음에 대한 감지와 그에 대한 조치는 눈을 감은 순간부터 약 0.9초쯤에 이루어져야 합니다. 30 FPS의 영상을 기준으로 0.9/0.033 = 약 27프레임이 되고, 졸음운전 방지 알람이 동작할 시간까지 계산하여 약 25프레임 동안 EAR 값이 Threshold보다 작으면 운전자가 졸음운전 중이라고 판단하도록 설정하였습니다.
- 이 프로젝트에서는 졸음운전 상태를 감지하는 것을 넘어 졸음 수준을 세 단계로 분리했습니다.
- Drowsiness levels are identified by the following conditions.
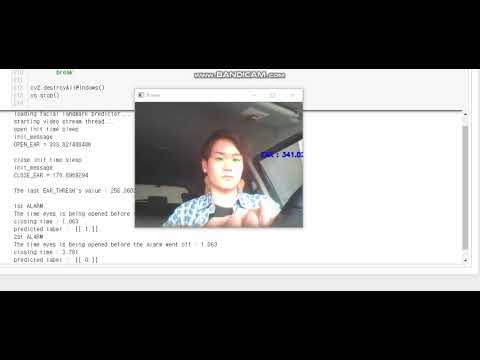
- The first alarm will sound(approximately 0.9 seconds) between level 1 and 2 of the drowsy phase.
- If you are dozing (sleeping and waking again and again) in less than 15 seconds, the drowsiness phase starts at level 1 and then the next alarm goes up to 0.
- The first alarm is level 2 and the second alarm is level 1 and the third alarm makes level 0 sound when driving drowsy between 15 and 30 seconds.
- If you have not been drowsy for more than 30 seconds, set level 2.
- 졸음 단계는 눈을 감고 있는 시간과 졸음운전 전까지 눈을 뜨고 있던 시간에 따라 구분되고, 졸음 2 -> 0으로 갈수록 알람의 세기는 세집니다.
- To distinguish drowsiness level, I used K-Nearest Neighbor(KNN) supervised learning algorithm.
- 래프를 기준으로 실제 졸음 단계를 결정하기 위해서 지도 학습(Supervised Learning) 알고리즘 중 하나인 K-Nearest Neighbor(이하 KNN) 알고리즘을 사용하였습니다.
. 1. Create arrays with random (x, y)-coordinates.
- Labeling
- Define K value.
- Test KNN algorithm.
Synthesis
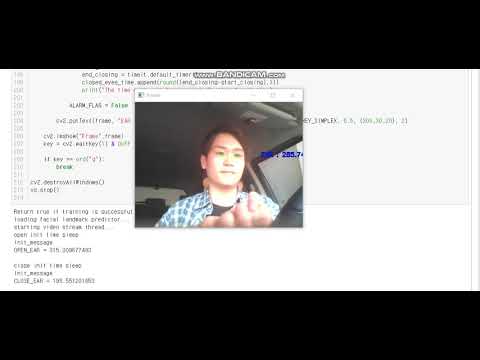
Test
Execution
- I run drowsiness_detector.ipynb just typing CTRL+ENTER.
- 전 jupyter notebook을 사용했기 때문에 일단 업로드 해두었습니다. 파이썬으로 실행하셔도 됩니다.