bytedance / Lightseq
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Lightseq
LightSeq: A High Performance Inference Library for Sequence Processing and Generation
LightSeq is a high performance inference library for sequence processing and generation implemented in CUDA. It enables highly efficient computation of modern NLP models such as BERT, GPT2, Transformer, etc. It is therefore best useful for Machine Translation, Text Generation, Dialog, Language Modelling, and other related tasks using these models.
The library is built on top of CUDA official library(cuBLAS, Thrust, CUB) and custom kernel functions which are specially fused and optimized for these widely used models. In addition to model components, we also provide codes manage model weights trained from deepleanring framework and servers as a custom backend for TensorRT Inference Server(referred to as TRTIS in the later discussion). With LightSeq, you can easily deploy efficient model services or develop your own model architectures just with a little code modification.
Features
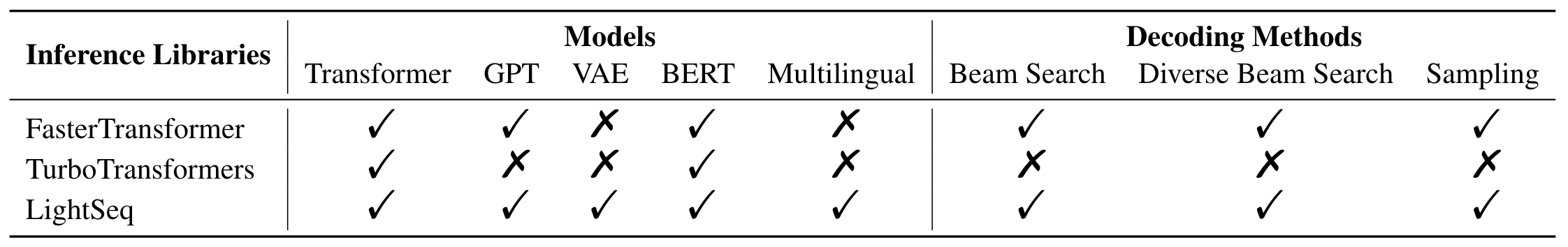
- Comprehensive sequence modeling support, including Bert, GPT, Transformer and their VAE variants.
- Various search methods, such as beam search, diverse beam search, topp/topk sampling.
- Out-of-the-box rich middlewares for model service based on TRTIS, such as dynamic batch, multi-model on single GPU.
- State of art inference performance compared with Deeplearning framework and other inference libraries.
The following is a support matrix of LightSeq compared with TurboTransformers and FasterTransformer.
Performance
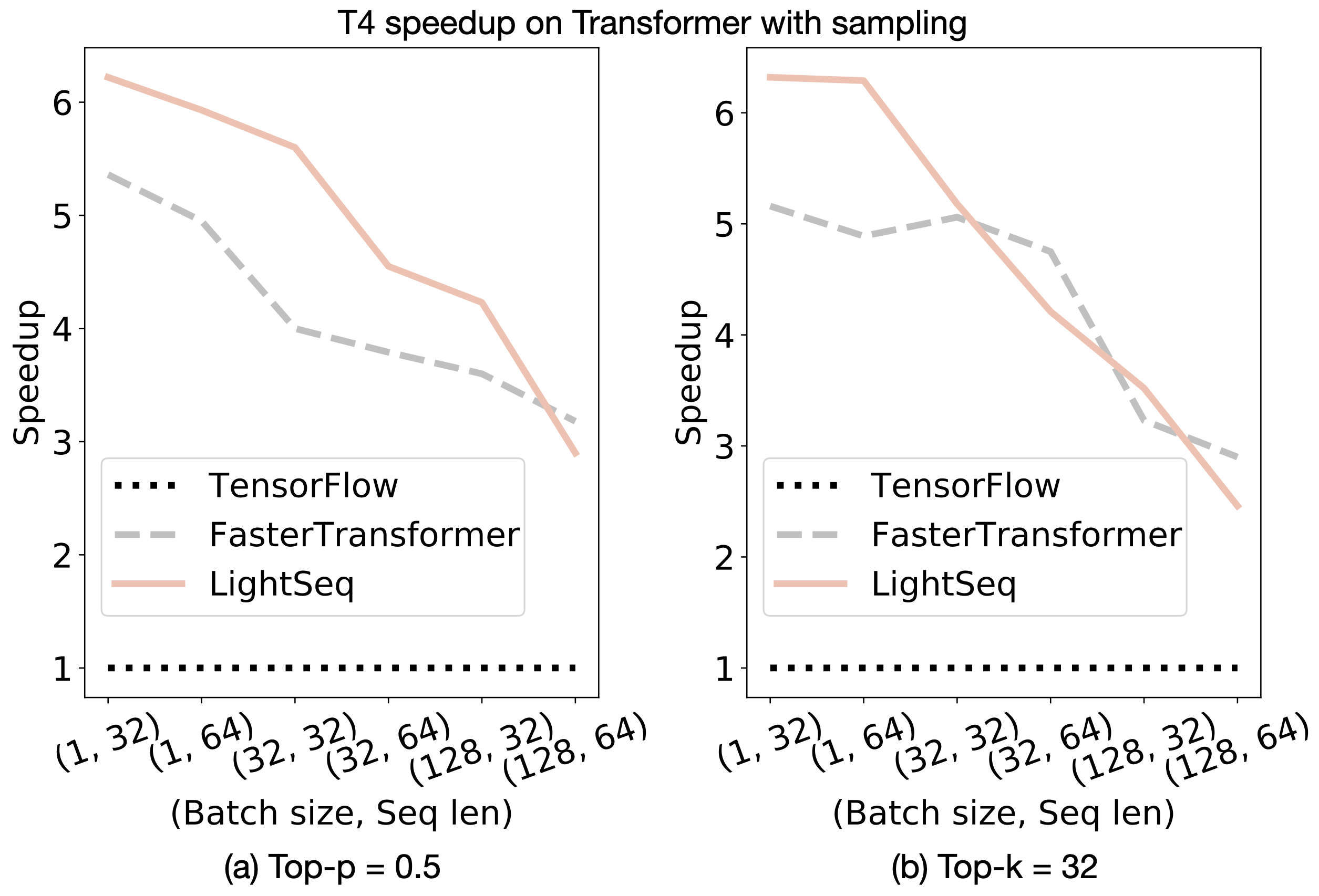
Here, we show our experimental results on neural machine translation and text generation. The models of these two tasks are Transformer-base, but use beam search and sampling search methods respectively. We choose Tensorflow and FasterTransformer as a comparison. The implementation from tensor2tensor was used as the benchmark of Tensorflow.
More results is available here.
- Neural machine translation


- Text generation
Code Structure
├── CMakeLists.txt # cmake build file
├── CONTRIBUTING.md
├── example
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── decoder_example.cc.cu # transformer decoder only example
│ ├── gpt_generation.cc.cu # GPT generation example
│ ├── gptlm_example.cc.cu # GPT language model example
│ ├── transformer_example.cc.cu # Transformer translation example
│ └── transformer_generate_example.cc.cu # Transformer generation example
├── kernels
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── common.h # common kernel functions
│ ├── gptKernels.cc.cu # GPT kernel functions
│ ├── gptKernels.h
│ ├── transformerKernels.cc.cu # Transformer kernel functions
│ └── transformerKernels.h
├── LICENSE
├── model
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── decoder.cc.cu # Transformer decoder
│ ├── decoder.h
│ ├── encoder.cc.cu # Transformer encoder
│ ├── encoder.h
│ ├── gpt_encoder.cc.cu # GPT encoder
│ └── gpt_encoder.h
├── NOTICE
├── proto
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── gpt.proto # proto file to save GPT model
│ ├── gpt_weight.cc # GPT weight class
│ ├── gpt_weight.h
│ ├── transformer.proto # # proto file to save Transformer model
│ ├── transformer_weight.cc # Transformer weight class
│ └── transformer_weight.h
├── pywrapper
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── transformer.cc.cu # python wrapper for Transformer
│ ├── transformer_decoder.cc.cu # python wrapper for Transformer decoder
│ └── wrapper.cc # pybind registeration
├── README.md
├── server # custom engine for Triton
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── custom.h # Triton dependeny
│ ├── decoder_generate_server.cc.cu
│ ├── generate_server.cc.cu
│ ├── gpt_generate_server.cc.cu
│ ├── gptlm_server.cc.cu
│ ├── libserver.ldscript # Triton dependeny
│ ├── model_config_cuda.h # Triton dependeny
│ ├── model_config.h # Triton dependeny
│ ├── model_config.proto # Triton dependeny
│ └── transformer_server.cc.cu
└── tools
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── util.cc.cu
└── util.h
Quick Start
Run python wrapper
We provide python api to call lightseq, and you only need to install lightseq with pip. Because lightseq run on GPU, make sure you have GPU driver not older than 418.40.04
pip install lightseq
And check these files proto/*.proto to prepare your model weights. We provide an example weight file for you to test.
curl -OL https://github.com/bytedance/lightseq/releases/download/v0.0.1/transformer_weight.tar.gz
tar -zxvf transformer_weight.tar.gz
Finally you can run lightseq in only a few lines!
import lightseq
import numpy as np
test_input = np.array([[5001, 2, 36, 5002]])
transformer = lightseq.Transformer("transformer.pb", 32) # 32 is max batch size, it will decide GPU memory occupancy.
result = transformer.infer(test_input)
Python api doesn't support GPT for now, and we will get it ready as soon as possible.
Run inference server
Requirements
- Install Docker and nvidia-docker.
- GPU driver version >= 410.48
- Login to the NGC registry.
To avoid problems caused by inconsistent environments, you can use the pre-built TRTIS container from NVIDIA GPU Cloud (NGC). To start the given container, you need to install nvidia-docker and make your GPU driver version >= 410.48
docker pull nvcr.io/nvidia/tensorrtserver:19.05-py3
#
docker run --gpus '"device=0"' -it --rm -p8000:8000 -p8001:8001 -p8002:8002 -v
/${current}/${path}:/quick_start nvcr.io/nvidia/tensorrtserver:19.05-py3 /bin/bash
# inside container
cd /quick_start
Use our pre-build lib
To quickly deploy your model that supported by LightSeq currently, you can download the pre-built libraries from the GitHub release page corresponding to the release version you are interested in. In each release version, we will upload binary executable example and dynamic link library of models which is a custom backend of TRTIS.
wget https://github.com/bytedance/lightseq/releases/download/${VERSION}/${VERSION}_libs.tar.gz
tar -zxvf ${VERSION}_libs.tar.gz
Run local inference demo
To run local inference demo, you need to prepare model weights saved in custom proto defined by LightSeq and input token ids. We provide a GPT-LM model and its corresponding input token ids:
wget https://github.com/bytedance/lightseq/releases/download/v0.0.1/v0.0.1_gptlm.pkg.tar.gz
tar -zxvf v0.0.1_gptlm.pkg.tar.gz
# fp32 example
./{VERSION}_libs/gptlm_example.fp32 ./v0.0.1_gptlm.pkg/gpt.pb ./v0.0.1_gptlm.pkg/test_case
# fp16 example
./{VERSION}_libs/gptlm_example.fp16 ./v0.0.1_gptlm.pkg/gpt.pb ./v0.0.1_gptlm.pkg/test_case
To run the end-to-end model server based on TRTIS, you need to prepare a custom backend model repository like this:
models/
<model-name>/
config.pbtxt # configuration
xxx # model weights
1/
libyyy.so # custom dynamic link library
With the pre-built libraries and example weights mentioned above, you can easily run a server:
mkdir -p ./model_zoo/gptlm/1
wget https://github.com/bytedance/lightseq/releases/download/v0.0.1/v0.0.1_gptlm.config.pbtxt
mv v0.0.1_gptlm.config.pbtxt model_zoo/gptlm/config.pbtxt
cp ./v0.0.1_gptlm.pkg/gpt.pb model_zoo/gptlm/gpt.pb
cp ./{VERSION}_libs/libgptlm.so.fp32 model_zoo/gptlm/1/libgptlm.so
# or fp16 server
# cp ./{VERSION}_libs/libgptlm.so.fp16 model_zoo/gptlm/1/libgptlm.so
export MODEL_ZOO="/quick_start/model_zoo"
trtserver --model-store=${MODEL_ZOO}
After starting server, Invoking the TRTIS client will get the inference result.
Serve your own model
In order to serve your own model, you need to export model trained from deeplearning framework(E.g. TenforFlow, PyTorch) to custom model proto defined by LightSeq. Furthermore, you may need to build from source code if you want to modify the model architectures or serve a new model not supported by LightSeq currently.
Limitations and Future Plans
LightSeq does not support CPU inference for now and its compilation relies heavily on TRTIS, we will try to solve these problems in future. Furthermore, the following will be the focus of our future work:
- Support more model architectures and decoding search algorithms.
- Int8 inference.
- Device deployment.
Contact
Check this Blog for more technical details of LightSeq. Join the lark group in the blog to reach us instantly(lark registration required).
Any questions or suggestions, please feel free to contact us. [email protected], [email protected]

