afollestad / Recyclical
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Recyclical
Recyclical
recyclical: an easy-to-use, extensible Kotlin DSL for setting up and manipulating RecyclerViews.
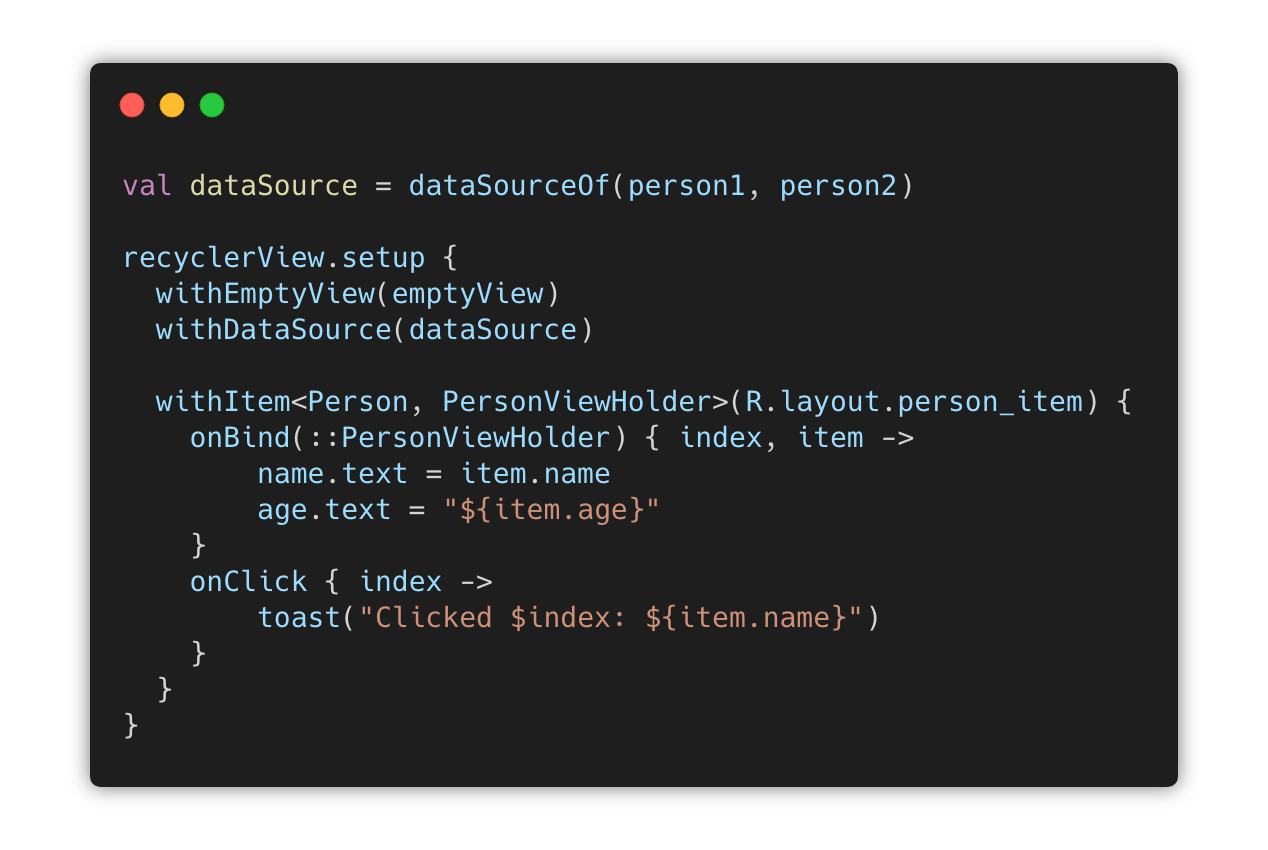
Table of Contents
Core
- Gradle Dependency
- The Basics
- More Options
- Child View Clicks
- Multiple Item Types
- DataSource
- SelectableDataSource
- Stable IDs
Swipe
Core
Gradle Dependency
Add this to your module's build.gradle file:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad:recyclical:1.1.1'
}
The Basics
First, declare an Item class:
data class Person(
var name: String,
var arg: Int
)
Second, a layout and a View Holder:
<LinearLayout ...>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_name"
... />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_age"
... />
</LinearLayout>
class PersonViewHolder(itemView: View) : ViewHolder(itemView) {
val name: TextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.text_name)
val age: TextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.text_age)
}
Finally, you can begin using the DSL API:
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// dataSourceTypedOf(...) here creates a DataSource<Person>
val dataSource = dataSourceTypedOf(
Person("Aidan", 24),
Person("Nina", 24)
)
// setup{} is an extension method on RecyclerView
recyclerView.setup {
withDataSource(dataSource)
withItem<Person, PersonViewHolder>(R.layout.person_item_layout) {
onBind(::PersonViewHolder) { index, item ->
// PersonViewHolder is `this` here
name.text = item.name
age.text = "${item.age}"
}
onClick { index ->
// item is a `val` in `this` here
toast("Clicked $index: ${item.name}")
}
onLongClick { index ->
// item is a `val` in `this` here
toast("Long clicked $index: ${item.name}")
}
}
}
}
}
More Options
There are other things you can give to the setup extension:
recyclerView.setup {
// Custom layout manager, rather than the default which is a vertical LinearLayoutManager
withLayoutManager(GridLayoutManager(context, 2))
// Assigns a view that is made visible when the data source has no content, else is hidden (gone)
withEmptyView(view)
// Global click listener for any item type. Individual item click listeners are called first.
withClickListener { index, item -> }
// Global long click listener for any item type. Individual item long click listeners are called first.
withLongClickListener { index, item -> }
// Add an animation used to animate the group's children after the first layout.
withLayoutAnimation(R.anim.your_anim, durationRes = android.R.integer.config_animShortTime)
}
Child View Clicks
There are many cases in which you'd want to get callbacks for a child view in your list items getting clicked, such as the sender icon in a list of emails.
class EmailViewHolder(itemView: View) : ViewHolder(itemView) {
val icon = itemView.findViewById<ImageView>(R.id.icon)
}
recyclerView.setup {
withItem<EmailItem, EmailViewHolder>(R.layout.email_item_layout) {
...
onChildViewClick(EmailViewHolder::icon) { index, view ->
// `this` includes `item` along with selection-related methods discussed below in SelectableDataSource
// `view` argument here is automatically an `ImageView`
}
}
}
Multiple Item Types
You can mix different types of items - but you need to specify view holders and layouts for them too:
// dataSourceOf(...) without "typed" creates a DataSource<Any>
val dataSource = dataSourceOf(
Car(2012, "Volkswagen GTI"),
Motorcycle(2018, "Triumph", "Thruxton R"),
Person("Aidan", 24)
)
recyclerView.setup {
withDataSource(dataSource)
withItem<Person, PersonViewHolder>(R.layout.person_item_layout) {
onBind(::PersonViewHolder) { index, item ->
name.text = item.name
age.text = "${item.age}"
}
}
withItem<Motorcycle, MotorcycleViewHolder>(R.layout.motorcycle_item_layout) {
onBind(::MotorcycleViewHolder) { index, item ->
year.text = "${item.year}"
make.text = item.make
model.text = item.model
}
}
withItem<Car, CarViewHolder>(R.layout.car_item_layout) {
onBind(::CarViewHolder) { index, item ->
year.text = "${item.year}"
name.text = item.name
}
}
}
DataSource
DataSource is an interface which provides data and allows manipulation of the data, to display in a RecyclerView.
Being an interface means you make your own implementations of it, you can mock it in tests, you could even provide it
via Dagger to a presenter and manipulate the RecyclerView outside of your UI layer.
Construction
The included implementation of data source operates on a List of objects (of any type).
// Empty by default, but can still add, insert, etc.
val dataSource: DataSource<Any> = emptyDataSource()
val dataSourceTyped: DataSource<Person> = emptyDataSourceTyped<Person>()
// Initial data set of items from a vararg list
val dataSource: DataSource<Any> = dataSourceOf(item1, item2)
val dataSourceTyped: DataSource<Person> = dataSourceTypedOf(item1, item2)
// Initial data set of items from an existing list
// Could also use dataSourceTypedOf(...)
val items = listOf(item1, item2)
val dataSource: DataSource<Any> = dataSourceOf(items)
val dataSourceTyped: DataSource<Person> = dataSourceTypedOf(items)
Manipulation
val dataSource: DataSource<ItemType> = // ...
// getters
val item: ItemType = dataSource[5]
val contains: Boolean = dataSource.contains(item)
val size: Int = dataSource.size()
val isEmpty: Boolean = dataSource.isEmpty()
val isNotEmpty: Boolean = dataSource.isNotEmpty()
val firstIndex: Int = dataSource.indexOfFirst { }
val lastIndex: Int = dataSource.indexOfLast { }
// mutation
val person = Person("Aidan", 24)
dataSource.add(person)
dataSource.set(listOf(person))
dataSource.insert(1, person)
dataSource.removeAt(1)
dataSource.remove(person)
dataSource.swap(1, 4)
dataSource.move(1, 4)
dataSource.clear()
// iteration
for (item in dataSource) { }
dataSource.forEach { } // emits all items
dataSource.forEachOf<Person> { } // only emits items that are a Person
// operators
val item: Any = dataSource[5] // get(5)
val contains: Boolean = item in dataSource // contains(item)
dataSource += person // add(person)
dataSource -= person // remove(person)
Diffing
When performing a set on the data set, you can opt to use diff utils:
dataSource.set(
newItems = newItems,
areTheSame = ::areItemsTheSame,
areContentsTheSame = ::areItemContentsTheSame
)
// Return true if items represent the same entity, e.g. by ID or name
private fun areItemsTheSame(left: Any, right: Any): Boolean {
return when (left) {
is Person -> {
right is Person && right.name == left.name
}
else -> false
}
}
// Return true if all contents in the items are equal
private fun areItemContentsTheSame(left: Any, right: Any): Boolean {
return when (left) {
is Person -> {
right is Person &&
right.name == left.name &&
right.age == left.age
}
else -> false
}
}
This will automatically coordinate notifying of adds, moves, and insertions so that update of the data set is pretty and animated by the RecyclerView.
SelectableDataSource
A SelectableDataSource is built on top of a regular [DataSource]. It provides additional APIs
to manage the selection state of items in your list.
Construction
Construction methods for SelectableDataSource are the same as the DataSource ones, they just
include selectable in their names.
// Empty by default, but can still add, insert, etc.
// Could also use emptySelectableDataSourceTyped()
val dataSource: SelectableDataSource<Any> = emptySelectableDataSource()
val dataSourceTyped: SelectableDataSource<Person> = emptySelectableDataSourceTyped()
// Initial data set of items from a vararg list
// Could also use selectableDataSourceTypedOf(...)
val dataSource: SelectableDataSource<Any> = selectableDataSourceOf(item1, item2)
val dataSourceTyped: SelectableDataSource<Person> = selectableDataSourceTypedOf(item1, item2)
// Initial data set of items from an existing list
// Could also use selectableDataSourceTypedOf(...)
val items = listOf(item1, item2)
val dataSource: SelectableDataSource<Any> = selectableDataSourceOf(items)
val dataSourceTyped: SelectableDataSource<Person> = selectableDataSourceTypedOf(items)
Manipulation
There are some additional methods added on top of the DataSource methods:
val dataSource: SelectableDataSource<Any> = // ...
// Index operations
dataSource.selectAt(1)
dataSource.deselectAt(1)
dataSource.toggleSelectionAt(1)
val selected: Boolean = dataSource.isSelectedAt(1)
// Item operations, uses index operations under the hood
val item: Any = // ...
dataSource.select(item)
dataSource.deselect(item)
dataSource.toggleSelection(item)
val selected: Boolean = dataSource.isSelected(item)
// Mass operations
dataSource.selectAll()
dataSource.deselectAll()
// Misc operations
val count: Int = dataSource.getSelectionCount()
val hasSelection: Boolean = dataSource.hasSelection()
// Set a callback invoked when something is selected or deselected
dataSource.onSelectionChange { dataSource -> }
Use in Binding
During binding of your items, you can access selection states even if you don't have a direct
reference to your DataSource.
In onBind blocks, this is done with extensions in ViewHolder which provide functions to check
selection state and select/deselect the current item that is being bound.
In onClick and onLongClick blocks, this is done using a type that is passed as this which provides the same set
of functions.
recyclerView.setup {
withEmptyView(emptyView)
withDataSource(dataSource)
withItem<MyListItem, MyViewHolder>(R.layout.my_list_item) {
onBind(::MyViewHolder) { index, item ->
// Selection-related methods that can be used here:
isSelected()
select()
deselect()
toggleSelection()
hasSelection()
}
onClick { index ->
// Selection-related methods that can be used here:
isSelected()
select()
deselect()
toggleSelection()
hasSelection()
}
onChildViewClick(MyViewHolder::someView) { index, view ->
// The same methods used in onClick can be used here as well
}
onLongClick { index ->
// The same methods used in onClick can be used here as well
}
}
}
Stable IDs
Stable IDs are an optimization hint for RecyclerView. When using stable IDs, you're telling
the view that each ViewHolder ID is unique and will not change. In Recyclical, to can use stable IDs
by having all of your items provide a unique ID for themselves.
data class AnItemWithAnId(
val id: Int,
val name: String
)
recyclerView.setup {
withDataSource(dataSource)
withItem<AnItemWithAnId, MyViewHolder>(R.layout.my_item_layout) {
onBind(::MyViewHolder) { index, item -> ... }
// The key is this, which says the `id` field of your item represents a unique ID.
hasStableIds { it.id }
}
}
If you have more than one item that your RecyclerView can hold, all need to define hasStableIds.
Swipe
The swipe module provides extensions to setup swipe actions, like swipe to delete.
Gradle Dependency
Add this to your module's build.gradle file:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad:recyclical-swipe:1.0.1'
}
The Basics
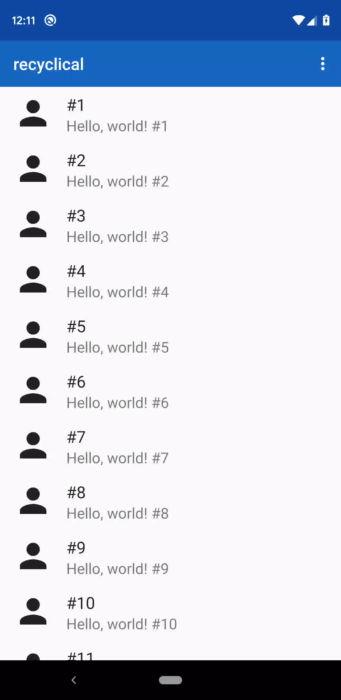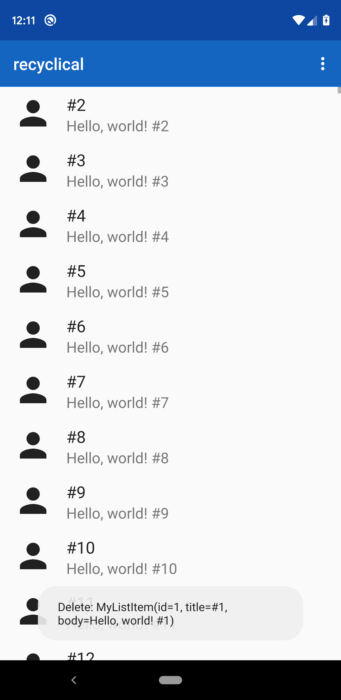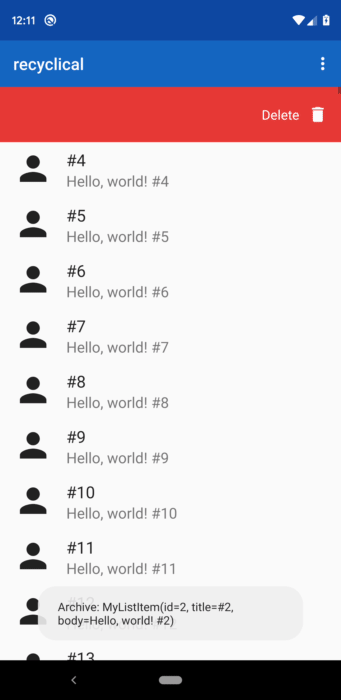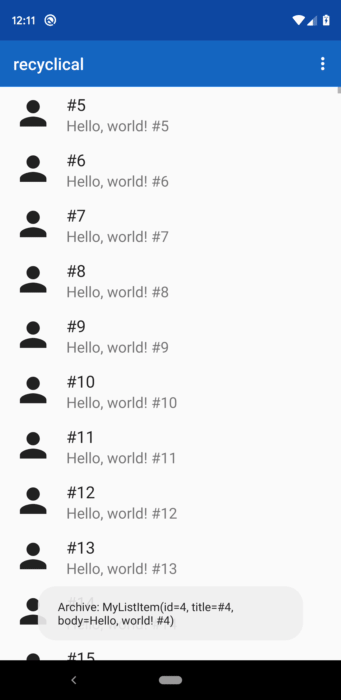
This example below sets up swipe to delete, so that it works if you swipe either right or left.
A delete icon and delete text would be shown over a red gutter. The callback returning true means
that the item should be removed from the DataSource when the action triggers.
list.setup {
...
withSwipeAction(LEFT, RIGHT) {
icon(R.drawable.ic_delete)
text(R.string.delete)
color(R.color.md_red)
callback { index, item -> true }
}
}
You can target specific item types with withSwipeActionOn, too:
withSwipeActionOn<MyItem>(LEFT, RIGHT) {
icon(R.drawable.ic_delete)
text(R.string.delete)
color(R.color.md_red)
callback { index, item -> true }
}
With withSwipeActionOn, item in the callback is a MyItem instead of Any as well.
Customization
As you saw above, you can use icons, text, and background colors easily. There are more details you can customize about your swipe actions, mainly around text:
list.setup {
...
withSwipeAction(LEFT, RIGHT) {
text(
res = R.string.delete,
color = R.color.black,
size = R.dimen.small_text_size,
typefaceRes = R.font.roboto_mono
)
}
}



