Veritatem Dies Aperit - Temporally Consistent Depth Prediction Enabled by a Multi-Task Geometric and Semantic Scene Understanding Approach
Requires an NVIDIA GPU, Python 3, CUDA CuDNN, PyTorch 1.0, and OpenCV.
Other libraries such as visdom are also optionally used in the code. If you wish to use visdom to plot curves and display results, this needs to be set in the arguments via --display.
Method:
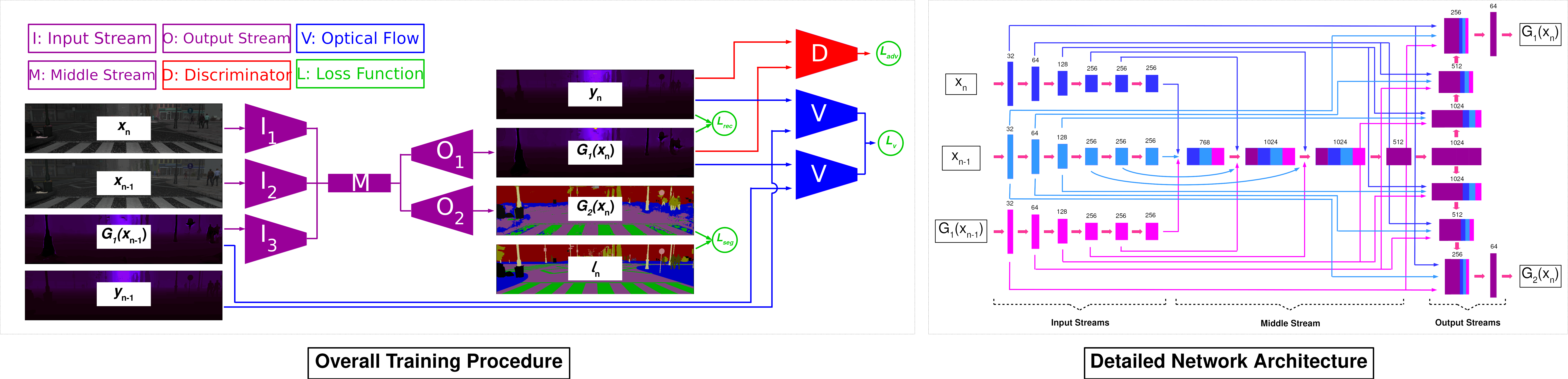
"Robust geometric and semantic scene understanding is ever more important in many real-world applications such as autonomous driving and robotic navigation. In this work, we propose a multi-task learning-based approach capable of jointly performing geometric and semantic scene understanding, namely depth prediction (monocular depth estimation and depth completion) and semantic scene segmentation. Within a single temporally constrained recurrent network, our approach uniquely takes advantage of a complex series of skip connections, adversarial training and the temporal constraint of sequential frame recurrence to produce consistent depth and semantic class labels simultaneously. Extensive experimental evaluation demonstrates the efficacy of our approach compared to other contemporary state-of-the-art techniques."
[Atapour-Abarghouei and Breckon, CVPR, 2019]
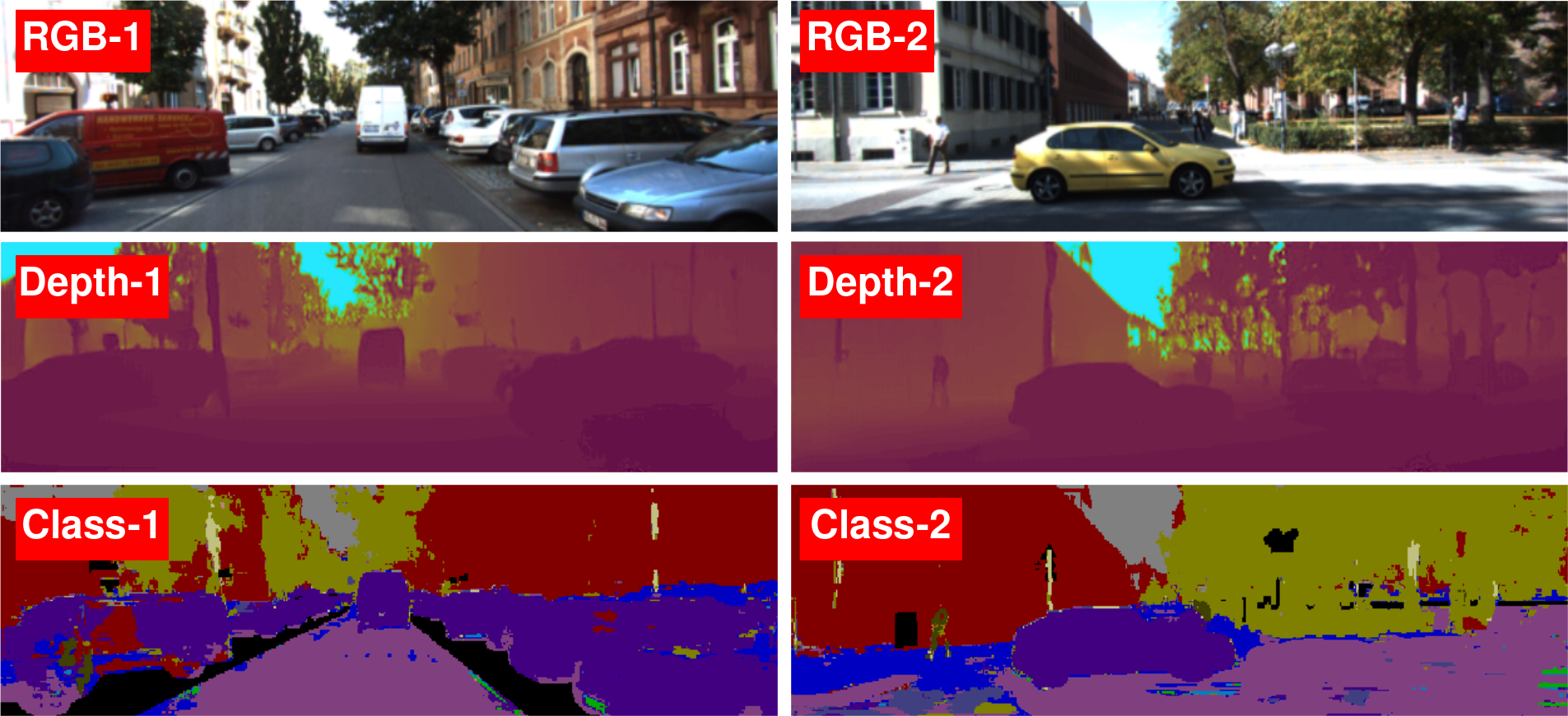 Example of the results of the approach
Example of the results of the approach
Instructions to train the model:
- First and foremost, this repository needs to be cloned:
$ git clone https://github.com/atapour/temporal-depth-segmentation.git
$ cd temporal-depth-segmentation
- A dataset needs to be prepared to be used for training. In our experiments, we use the SYNTHIA dataset. However, any other dataset containing correponding RGB, depth and class label images is suitable for training this model. We have provided a simple, albeit inefficient, python script (
data_processing/prepare_data.py) that processes the SYNTHIA data and generates a data root in accordance with our custom training dataset class (data/train_dataset.py). However, feel free to modify the script or the dataset class to fit your own data structure. Our custom dataset follows the following directory structure:
Custom Dataset
├── train
│ ├── 0
│ │ ├── Depth
│ │ │ ├── 000000.png
│ │ │ ├── 000001.png
│ │ │ ├── ...
│ │ ├── GT
│ │ │ ├── 000000.png
│ │ │ ├── 000001.png
│ │ │ ├── ...
│ │ ├── RGB
│ │ │ ├── 000000.png
│ │ │ ├── 000001.png
│ │ │ ├── ...
│ ├── 1
│ │ ├── Depth
│ │ │ ├── 000000.png
│ │ │ ├── 000001.png
│ │ │ ├── ...
│ │ ├── GT
│ │ │ ├── 000000.png
│ │ │ ├── 000001.png
│ │ │ ├── ...
│ │ ├── RGB
│ │ │ ├── 000000.png
│ │ │ ├── 000001.png
│ │ │ ├── ...
...
-
The training code can utilizes visdom to display training results and plots, in order to do which simply run
visdomand then navigate to the URL http://localhost:8097. If you intend to use this, the argument--displayneeds to be added to the command line. -
To train the model, run the following command:
$ python train.py --name=name --data_root=path/to/data
- All the arguments for the training are passed from the file
train_arguments.py. Please refer to this file to see what options are available to be passed in as arguments.
Instructions to test the model:
-
In order to easily test the model, we provide a set of pre-trained weights. The pre-trained are stored separately due to their large size.
-
The script entitled "download_pretrained_weights.sh" will download the required pre-trained model and automatically checks the downloaded file integrity using MD5 checksum.
-
Additionally, a sequence of example image frames is provided in the
examplesdirectory for testing. -
To test the model, run the following commands:
$ chmod +x ./download_pretrained_weights.sh
$ ./download_pretrained_weights.sh
$ python test.py --data_root=./examples --test_checkpoint_path=./pre_trained_weights/pre_trained_weights.pth --results_path=./results
The output results are written in a directory taken as an argument to the test harness ('./results' by default):
- Three separate directories are created to store the RGB, depth, and segmented images.
Example:
Supplementary Video - click image above to play.
This work is created as part of the project published in the following. The model has been re-trained to provide better quality visual results.
Reference:
Veritatem Dies Aperit - Temporally Consistent Depth Prediction Enabled by a Multi-Task Geometric and Semantic Scene Understanding Approach (A. Atapour-Abarghouei, T.P. Breckon), In Proc. IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019. [pdf]
@InProceedings{abarghouei19depth,
author = {Atapour-Abarghouei, A. and Breckon, T.P.},
title = {Veritatem Dies Aperit - Temporally Consistent Depth Prediction Enabled by a Multi-Task Geometric and Semantic Scene Understanding Approach},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
pages={3373--3384},
year = {2019},
publisher = {IEEE}
}