Scrawk / Terrain Topology Algorithms
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Terrain Topology Algorithms
Terrain-Topology-Algorithms
This project is collection of algorithms that can be used to describe the topology of a terrain. The result of these algorithms can then be used for rendering the terrain or as input to other algorithms.
The formulas were take from a book called Digital Terrain Analysis for Soil Science.
Version 2 adds more curvature types, landform and residual types as well as a better way to visualize the maps using a color gradient and rescaling the wide dynamic range using a logarithmic scale.
The colorized maps can be displayed using a cool to warm or black to white gradient.
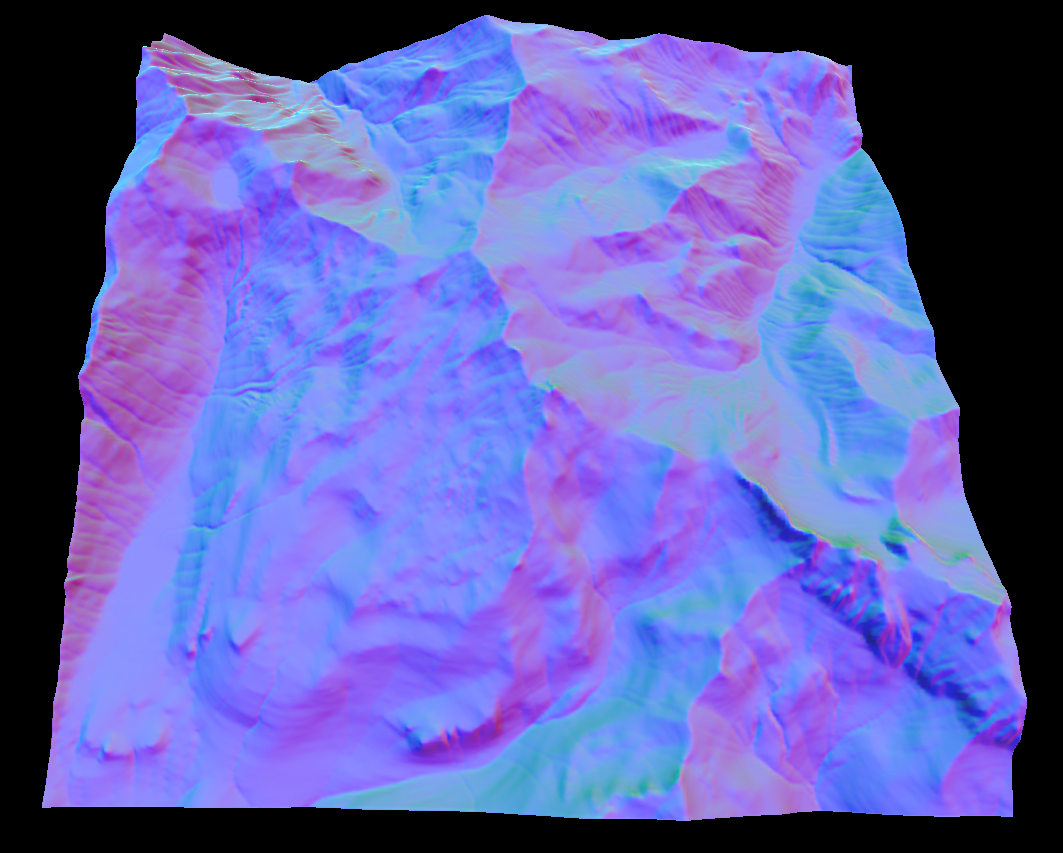
Normal map
The normal map is probably the most common algorithm used to describe the topology of a terrain because of its use in rendering. The normal's are a tangent space vector of the surface direction.
Its a good place to start as it requires calculating the first order derivatives of the terrains height map which are also used in many of other algorithms.
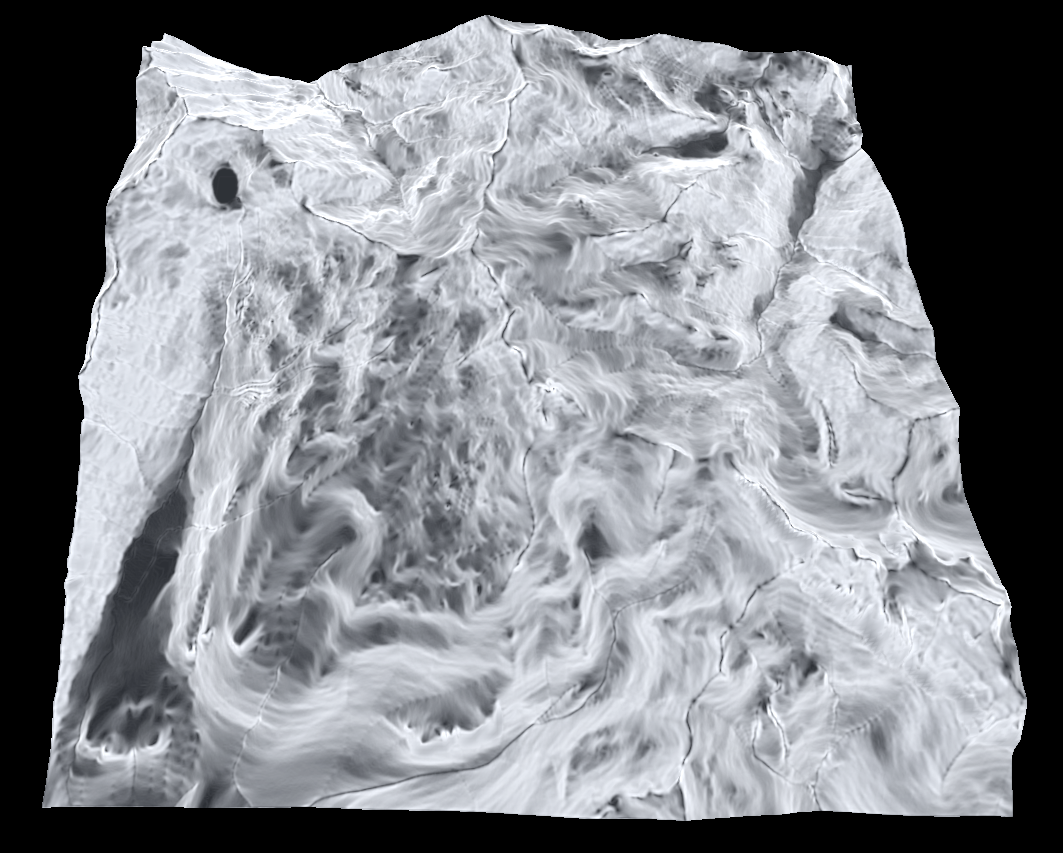
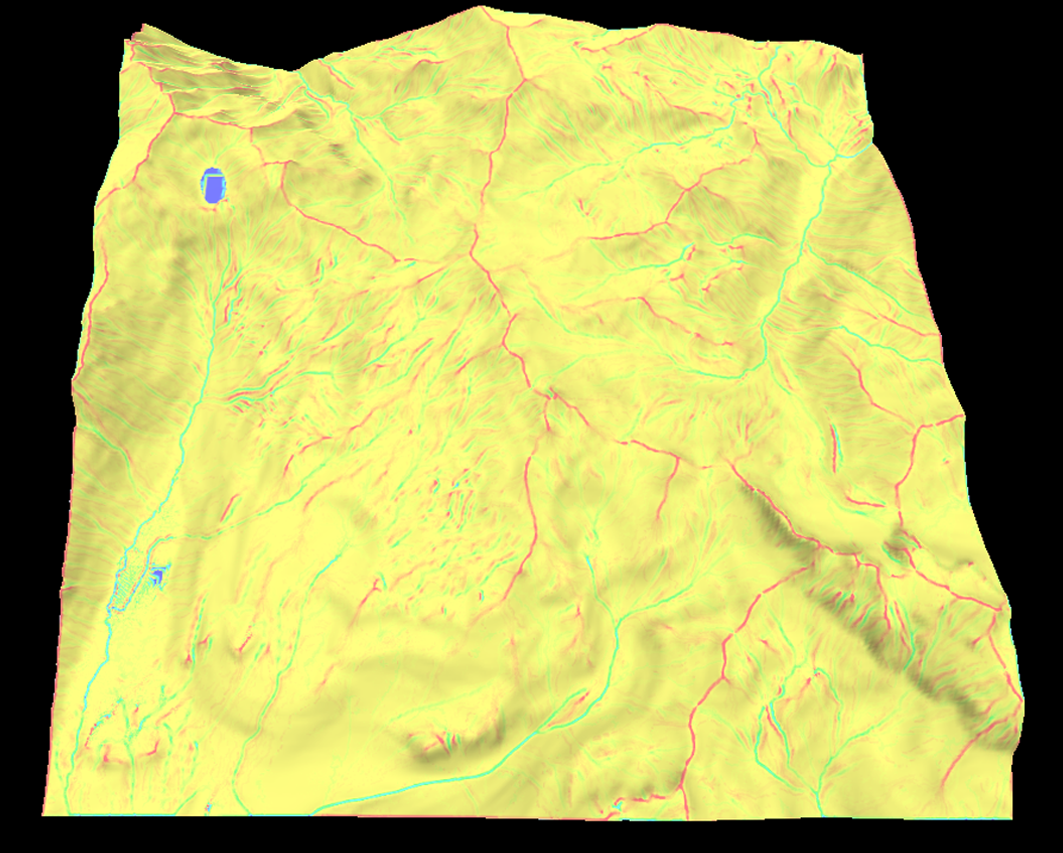
Slope map
The slope map describes the steepness of the terrain and is handy for texturing the terrain. Like the normal map this also requires the first order derivatives.
Aspect map
This is similar to the slope map but instead represents the horizontal gradient as opposed to the vertical gradient.
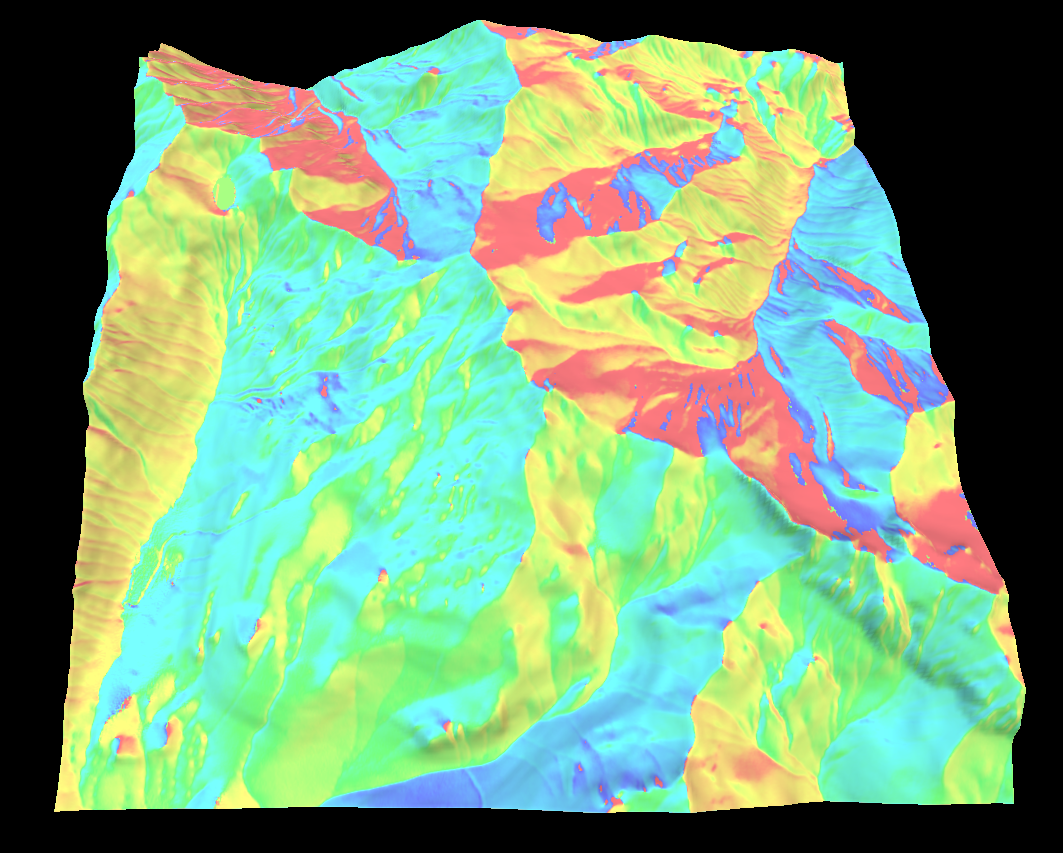
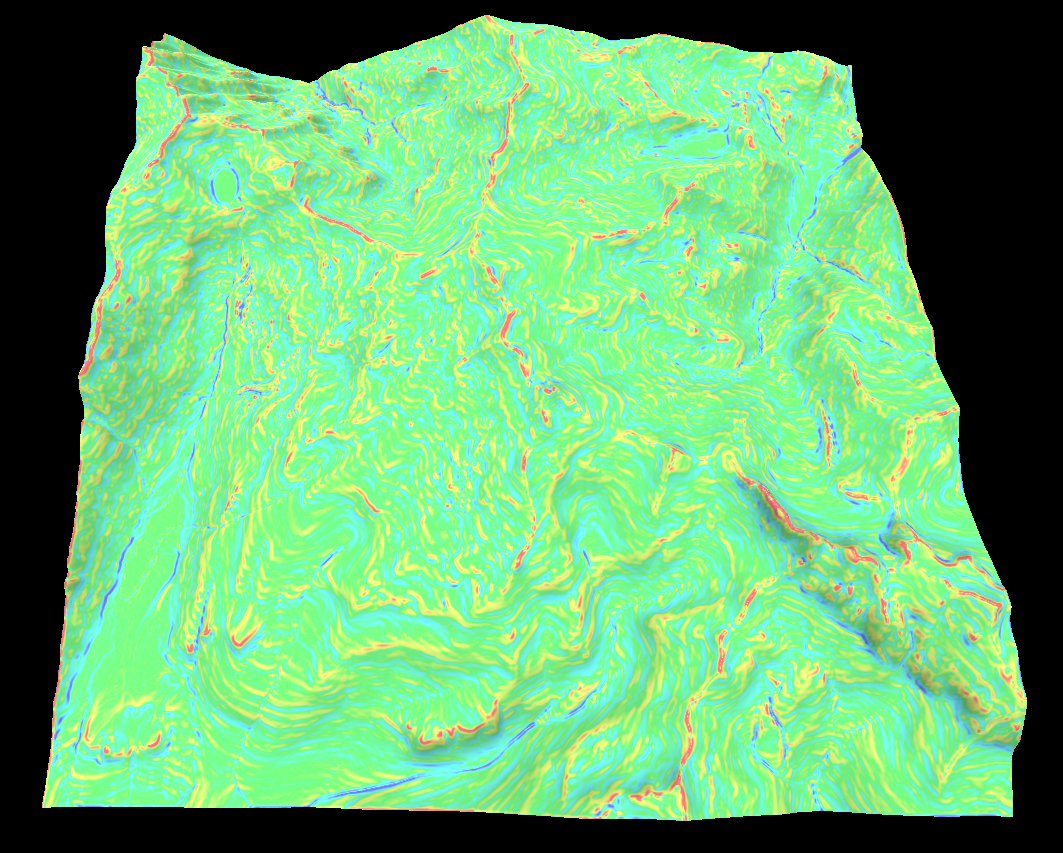
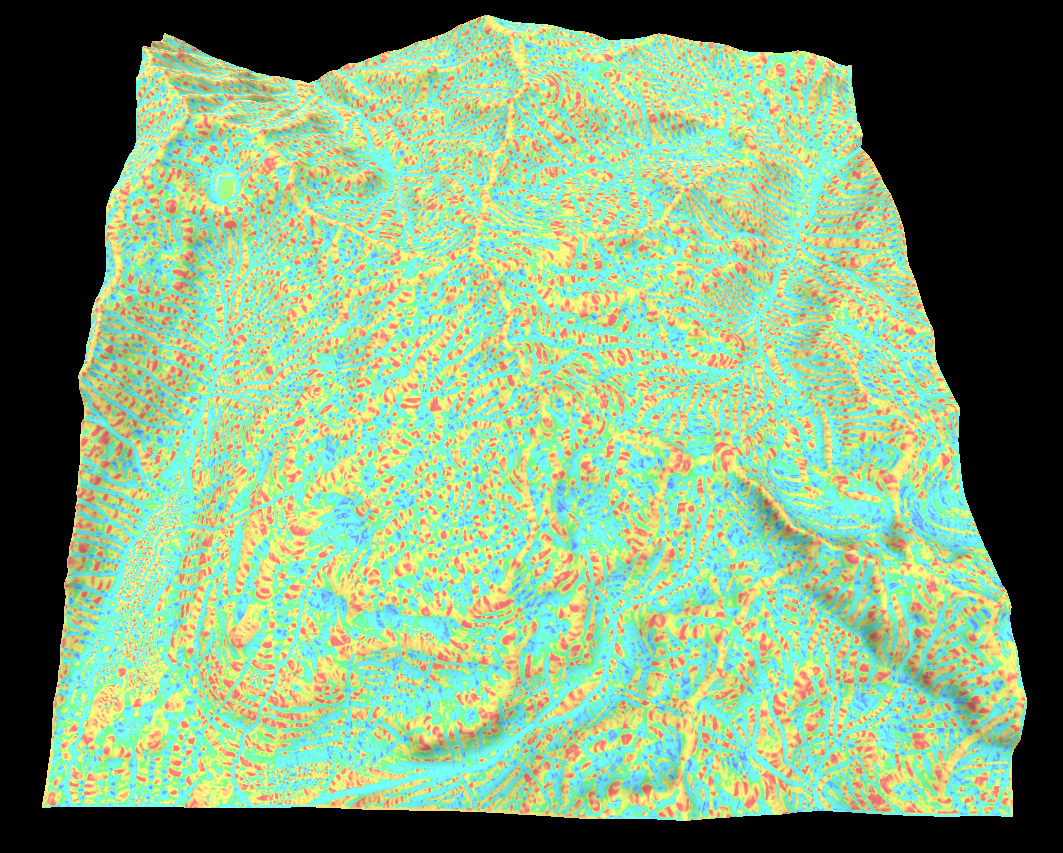
Curvature map
The curvature map represents the convexity/concavity of the surface. The curvature is a little more complicated to calculate and requires the first and second order derivatives of the terrains height.
There are a lot of ways to measure the curvature. The most useful are vertical, horizontal, mean, gaussian, minimal or maximal curvature but I have provide a few others.
Since curvature uses the second derivatives it can have quite a large dynamic range and can be negative which makes visualizing the map a bit tricky.
Below is the horizontal, vertical, gaussian, minimal and maximal curvatures in that order.
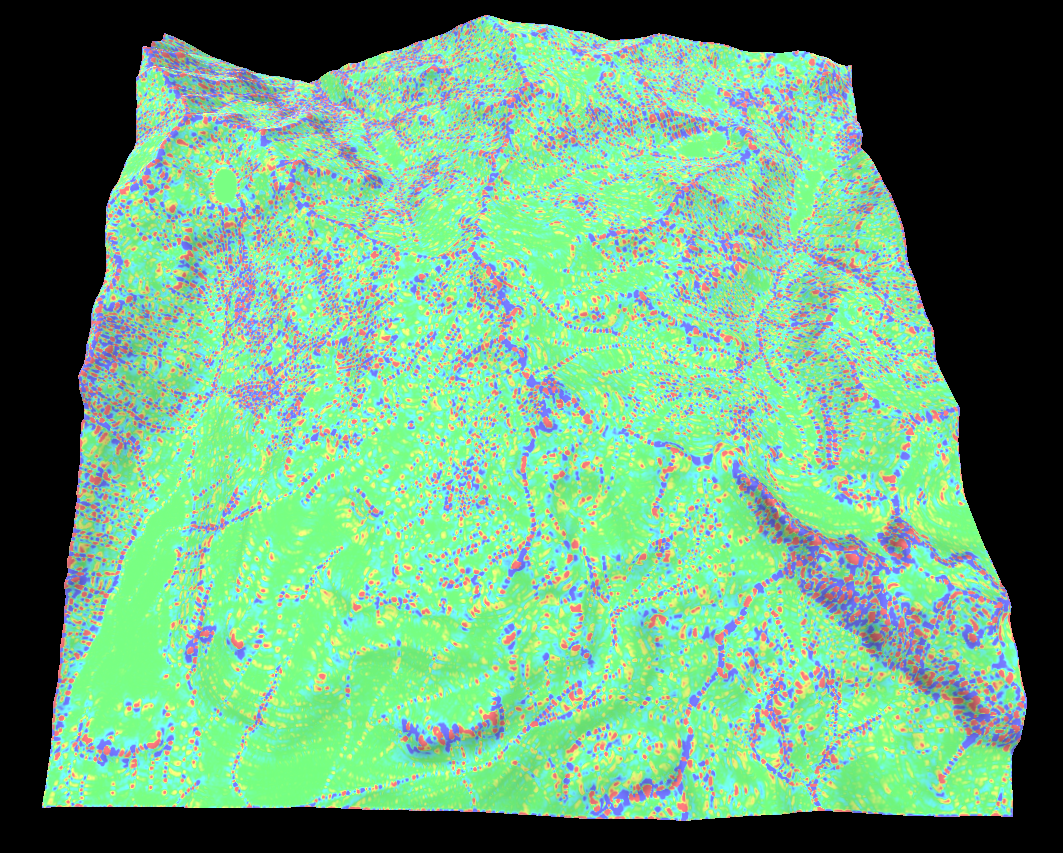
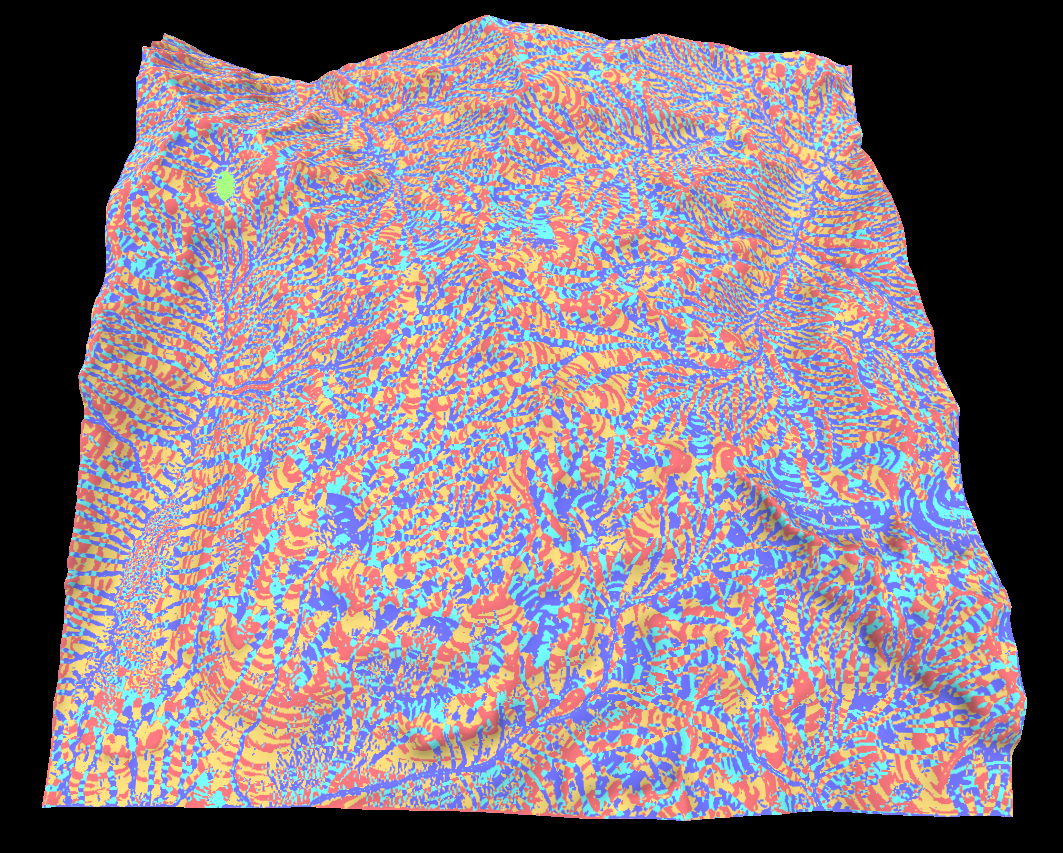
Landform map
The landform map combines some of the curvature values to try and classify the type of landform. For example if the landform is convex/concave or accumulative/dispersive.
The idea is the the shape of the landform determines how water flows over it which is a key indicator for soil type and depth.
Below is the shape index and accumulation landforms in that order.
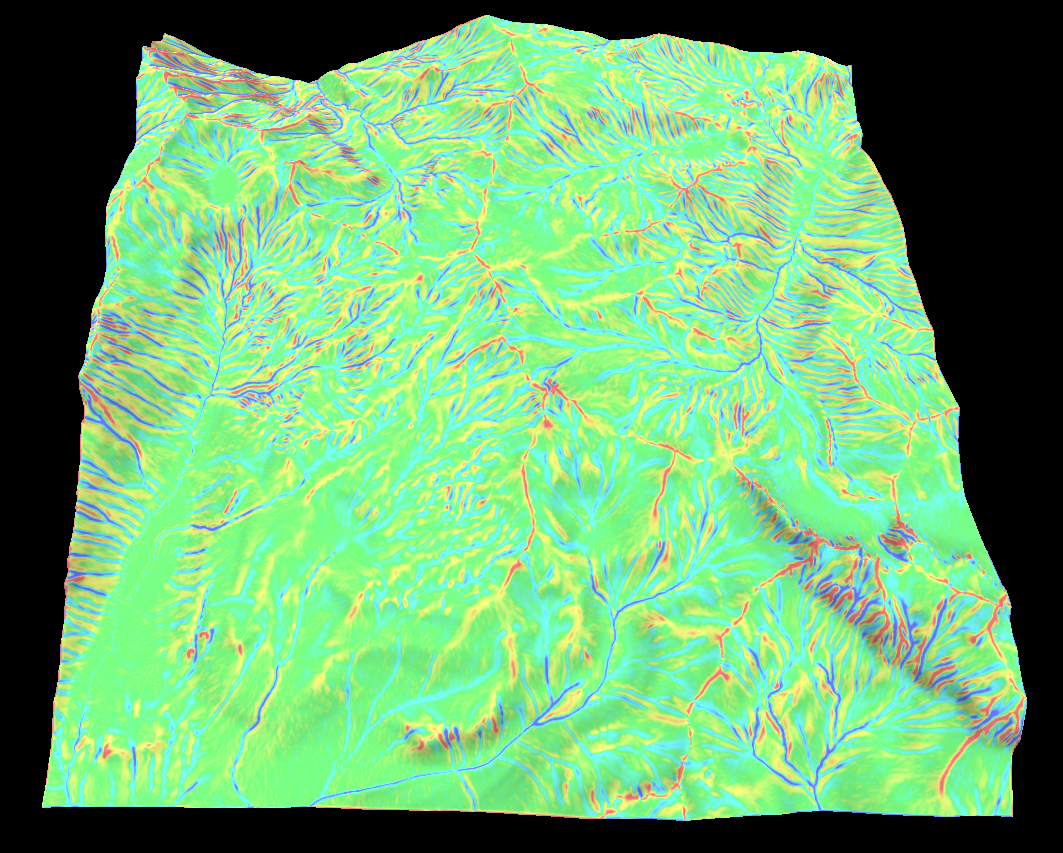
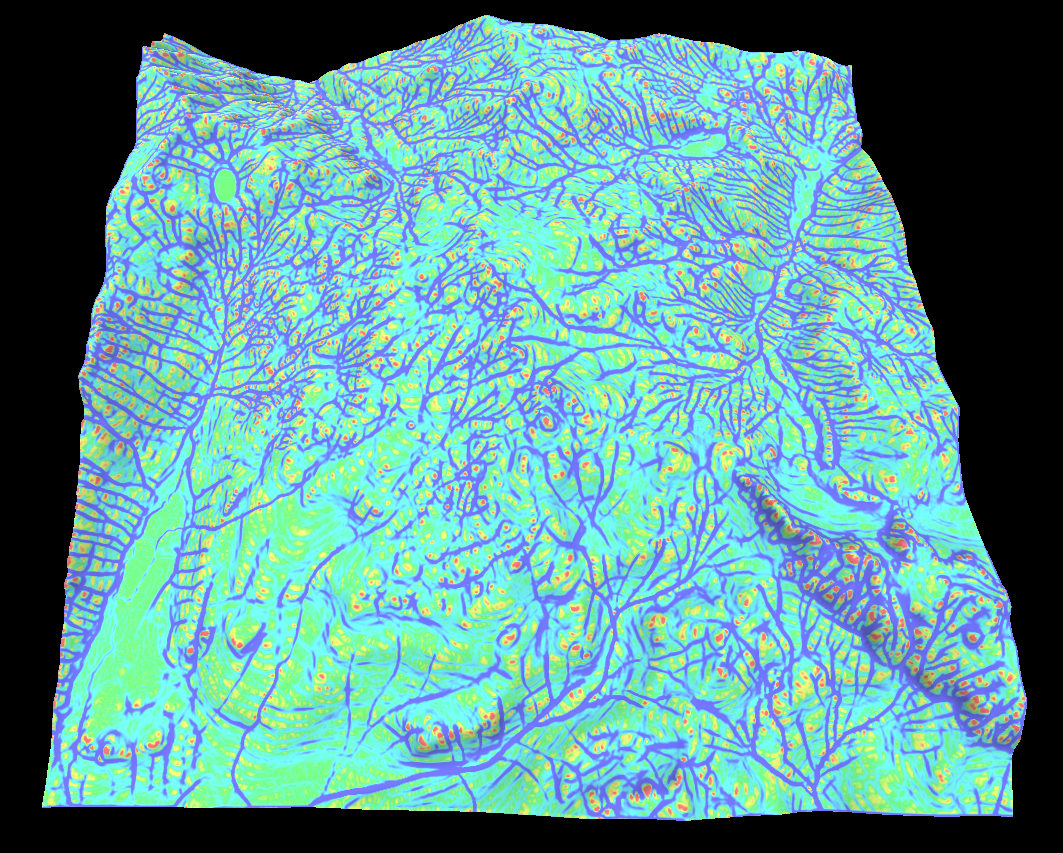
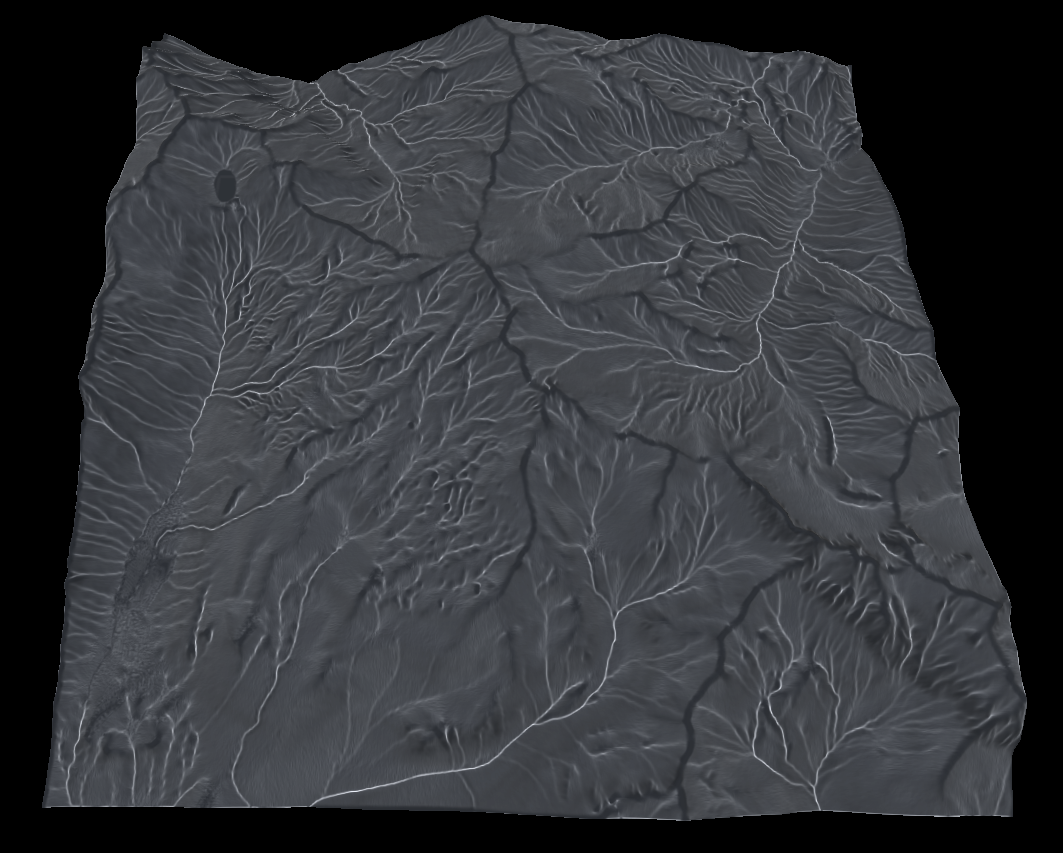
Flow map
This one is a bit different as its a iterative algorithm and is therefore a bit slow. Its works by simulating the path a small amount of water flowing over the terrain will take. The magnitude of the waters velocity can then be used to create a flow map.
Its a good way to make rivers or erosion effects.
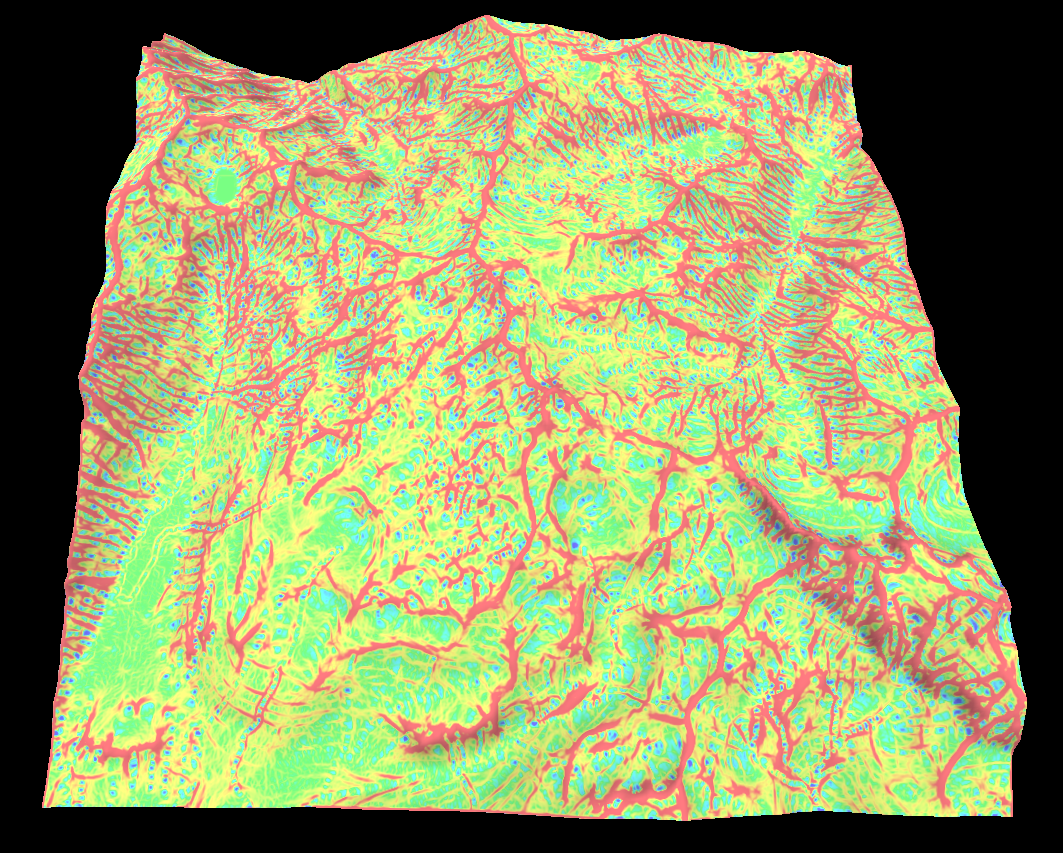
Residual map
The residual map takes the heights around a point in a given window and performs some sort of statistical analysis. For example the standard deviation represents the roughness of the terrain.
Options to calculate the mean, standard deviation, percentile and a few others are provided.
Below is the percentile map where the value represents the percentage of heights around a point that are lower.