lstkz / Ts Mongoose
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Ts Mongoose
ts-mongoose
Automatically infer TypeScript interfaces from mongoose schemas.
Installation
npm i ts-mongoose mongoose @types/mongoose
yarn add ts-mongoose mongoose @types/mongoose
The Problem
When using mongoose and Typescript, you must define schemas and interfaces. Both definitions must be maintained separately and must match each other. It can be error-prone during development and cause overhead.
ts-mongoose is a very lightweight library that allows you to create a mongoose schema and a typescript type from a common definition.
All types as created from 1-liner functions and does not depend on decorators❗️.
For example:
Type.string({ required: true }) returns {type: String, required: true}, which is the same definition required in the original mongoose library.
Example
Before:
import { Schema, model, Model, Document } from 'mongoose';
const AddressSchema = new Schema(
{
city: { type: String, required: true },
country: String,
zip: String,
},
{ _id: false, timestamps: true }
);
const PhoneSchema = new Schema({
phoneNumber: { type: Schema.Types.Number, required: true },
name: String,
});
const UserSchema = new Schema(
{
title: { type: String, required: true },
author: { type: String, required: true },
body: { type: String, required: true },
comments: [
{
body: { type: String, required: true },
date: { type: Date, required: true },
},
],
date: { type: Date, default: Date.now, required: true },
hidden: { type: Boolean, required: true },
meta: {
votes: { type: Schema.Types.Number },
favs: { type: Schema.Types.Number },
},
m: {
type: Schema.Types.Mixed,
required: true,
},
gender: {
type: Schema.Types.String,
required: true,
enum: ['male', 'female'],
},
otherId: {
type: Schema.Types.ObjectId,
required: true,
},
address: {
type: AddressSchema,
required: true,
},
phones: {
type: [PhoneSchema],
required: true,
},
},
{ timestamps: { createdAt: true } }
);
interface UserProps extends Document {
title: string;
author: string;
body: string;
// Duplicate all props from the above schema :(
}
const User: Model<UserProps> = model('User', UserSchema);
🎉🎉🎉 After:
import { createSchema, Type, typedModel } from 'ts-mongoose';
const genders = ['male', 'female'] as const;
const AddressSchema = createSchema(
{
city: Type.string({ required: true }),
country: Type.string(),
zip: Type.string(),
},
{ _id: false, timestamps: true }
);
const PhoneSchema = createSchema({
phoneNumber: Type.number({ required: true }),
name: Type.string(),
});
const UserSchema = createSchema(
{
title: Type.string({ required: true }),
author: Type.string({ required: true }),
body: Type.string({ required: true }),
comments: Type.array().of({
body: Type.string({ required: true }),
date: Type.date({ required: true }),
}),
date: Type.date({ default: Date.now as any }),
hidden: Type.boolean({ required: true }),
meta: Type.object().of({
votes: Type.number({ required: true }),
favs: Type.number({ required: true }),
}),
m: Type.mixed({ required: true }),
gender: Type.string({ required: true, enum: genders }),
otherId: Type.objectId({ required: true }),
address: Type.schema({ required: true }).of(AddressSchema),
phones: Type.array({ required: true }).of(PhoneSchema),
},
{ timestamps: { createdAt: true } }
);
const User = typedModel('User', UserSchema);
User.findById('123').then(user => {
if (user) {
user. // autocomplete here
}
});
API
- Each type has two forms: required and optional
{
// same as {type: String}
firstName: Type.string(),
// same as {type: String, required: true}
email: Type.string({ required: true }),
}
- Each type accepts the same options from mongoose
{
// same as {type: String, required: true, unique: true, index: true}
email: Type.string({ required: true, unique: true, index: true });
}
- Note that enum values need to be readonly array to be treated as literals by typescript
const genders = ['male', 'female'] as const;
{
// same as {type: String, enum: ['male', 'female']}
gender: Type.string({ enum: genders });
}
-
schema,object,arraytypes have a methodofwhere you must provide a child type
{
// same as {type: [String], required: true}
tags: Type.array({ required: true }).of(Type.string({ required: true }));
}
-
schema.of(ExampleSchema)has typical for Subdocument additional fields and methods. Setting{ _id: false }in SchemaOptions won't attach_idproperty in Subdocument
const AddressSchema = createSchema(
{ city: Type.string({ required: true }) },
{ _id: false, timestamps: true }
);
{
// same as {type: AddressSchema}
address: Type.schema().of(AddressSchema);
}
// address property has city property, other Subdocument methods and properties except '_id'
-
array.of(ExampleSchema)will return DocumentArray instead of standard array
const PhoneSchema = createSchema(
{ phoneNumber: Type.number({ required: true }) },
{ _id: false }
);
{
// same as {type: [PhoneSchema]}
phones: Type.array().of(PhoneSchema);
}
// phones property has such methods as create(), id(), but also those typical for arrays like map(), filter() etc
-
refis a special type for creating references
{
// same as [{type: Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: 'Comment'}]
comments: Type.array().of(
Type.ref(Type.objectId()).to('Comment', CommentSchema)
),
}
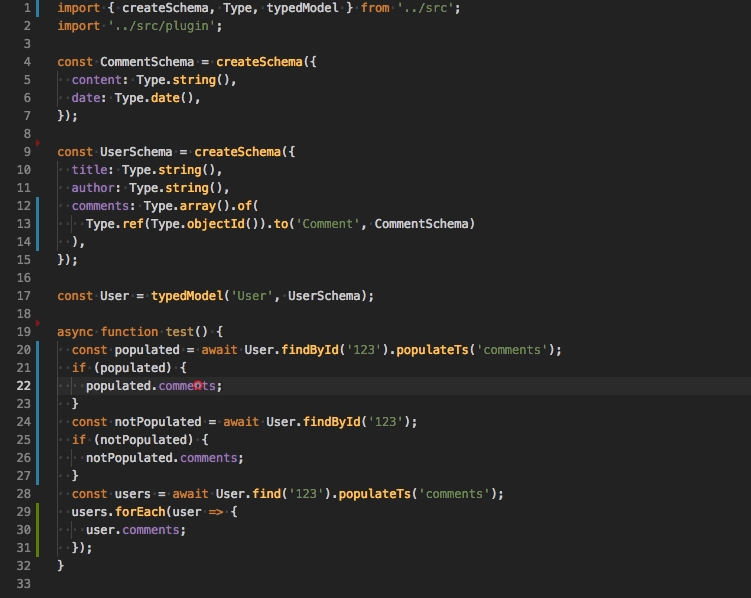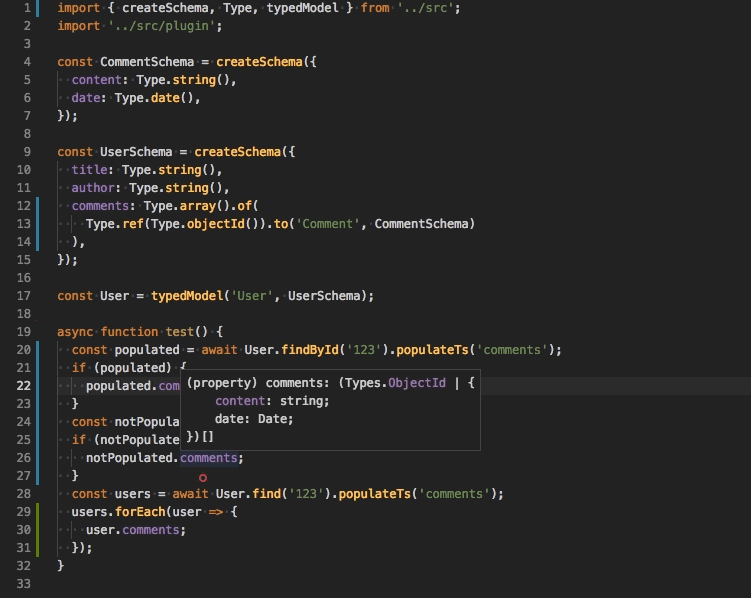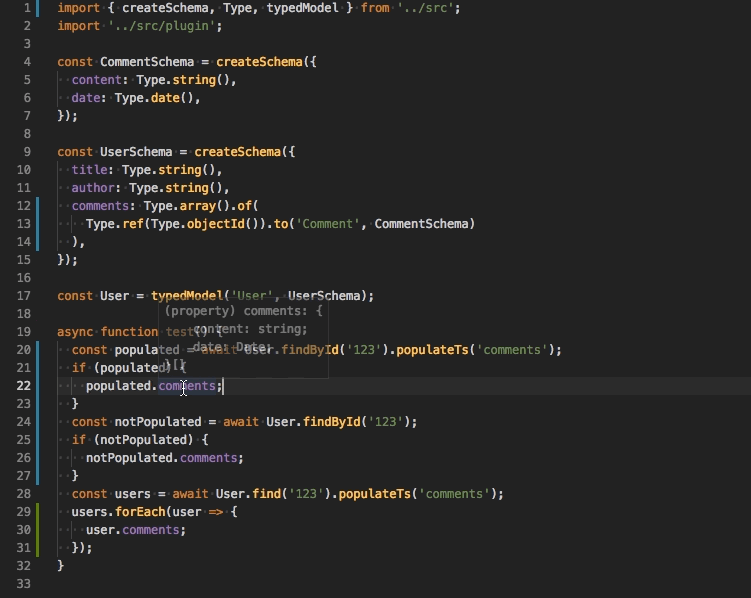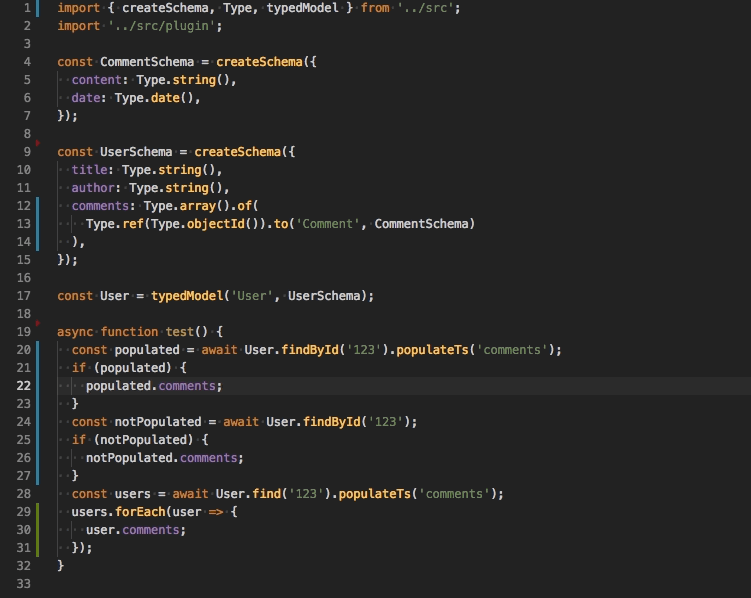
-
populateTs(property: string)use this function to populate a property and adjust the returned type automatically. Under the hood it calls only the nativepopulatemethod.
Method will be available if you import a special plugin.
// models.ts
import 'ts-mongoose/plugin';
User.find().populateTs('comments');
Extracting Document type
Use ExtractDoc to extract generated document type.
Use ExtractProps to extract generated base model properties.
Example:
import {
createSchema,
Type,
typedModel,
ExtractDoc,
ExtractProps,
} from 'ts-mongoose';
export const UserSchema = createSchema({
email: Type.string({ required: true }),
username: Type.string({ required: true }),
isBlocked: Type.boolean(),
});
export const User = typedModel('User', UserSchema);
export type UserDoc = ExtractDoc<typeof UserSchema>;
export type UserProps = ExtractProps<typeof UserSchema>;
// example function
async function blockUser(user: UserDoc) {
user.isBlocked = true;
// access all properties + Document methods and properties
await user.save();
}
function randomUser(): UserProps {
// must return `email`, `username`
// `isBlocked` is optional
return {
email: '[email protected]',
username: 'user1',
};
}
Refs
Refs and populations are supported.
Check code under example/example4.ts.
Custom Field
If you need to specify custom fields in the model, you can add a fake annotation.
It's only required if you add virtual fields or custom methods to the model.
const UserSchema = createSchema({
title: Type.string({ required: true }),
author: Type.string({ required: true }),
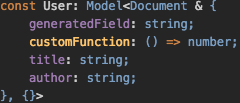
...({} as {
generatedField: string;
customFunction: () => number;
}),
});
const User = typedModel('User', UserSchema);
Static methods
If you need to have static custom methods on Model you can pass them as 5th parameter of typedModel function. It should automatically figured out returning value, but you can declare it too.
const UserSchema = createSchema({
name: Type.string({ required: true }),
age: Type.number({ required: true }),
});
const User = typedModel('User', UserSchema, undefined, undefined, {
findByName: function(name: string) {
return this.find({ name });
},
findOneByName: function(name: string) {
return this.findOne({ name });
},
countLetters: function(name: string, bonus?: number) {
return name.length + (bonus ? bonus : 0);
},
});
const u = await User.findOne({});
if (u) u.name;
Connection model
If you are using mongoose.createConnection(...), you can pass a <mongoose.Connection> as the 6th parameter of typedModel. Then the module will be added to that connection instead.
(Note: If using the connection parameter, the skipInit parameter will not be used)
import mongoose from 'mongoose'
import { typedModel } from 'ts-mongoose'
const UserSchema = createSchema({
name: Type.string({ required: true }),
age: Type.number({ required: true }),
});
const connection = mongoose.createConnection(`mongodb://localhost:27017/test`, {...})
const User = typedModel('User', UserSchema, undefined, undefined, undefined, connection);
console.log(connection.modelNames()) // Prints: [ 'User' ]
// Now you can use the model directly
User.find({ name: 'Peter' })
// Or through the connection
connection.model('User').find({ name: 'Peter' })
TODO
- support types: Map
MIT