IQSS / Zelig
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Zelig
Development:
Dev-Blog
Zelig workflow overview
All models in Zelig can be estimated and results explored presented using four simple functions:
-
zeligto estimate the parameters, -
setxto set fitted values for which we want to find quantities of interest, -
simto simulate the quantities of interest, -
plotto plot the simulation results.
Zelig 5 reference classes
Zelig 5 introduced reference classes. These enable a different way of working with Zelig that is detailed in a separate vignette. Directly using the reference class architecture is optional. They are not used in the examples below.
Zelig Quickstart Guide
Let’s walk through an example. This example uses the swiss dataset. It contains data on fertility and socioeconomic factors in Switzerland’s 47 French-speaking provinces in 1888 (Mosteller and Tukey, 1977, 549-551). We will model the effect of education on fertility, where education is measured as the percent of draftees with education beyond primary school and fertility is measured using the common standardized fertility measure (see Muehlenbein (2010, 80-81) for details).
Installing and Loading Zelig
If you haven't already done so, open your R console and install Zelig. We recommend installing Zelig with the zeligverse package. This installs core Zelig and ancillary packages at once.
install.packages('zeligverse')
Alternatively you can install the development version of Zelig with:
devtools::install_github('IQSS/Zelig')
Once Zelig is installed, load it:
library(zeligverse)
Building Models
Let’s assume we want to estimate the effect of education on fertility.
Since fertility is a continuous variable, least squares (ls) is an
appropriate model choice. To estimate our model, we call the zelig()
function with three two arguments: equation, model type, and data:
# load data
data(swiss)
# estimate ls model
z5_1 <- zelig(Fertility ~ Education, model = "ls", data = swiss, cite = FALSE)
# model summary
summary(z5_1)
## Model:
##
## Call:
## z5$zelig(formula = Fertility ~ Education, data = swiss)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -17.036 -6.711 -1.011 9.526 19.689
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 79.6101 2.1041 37.836 < 2e-16
## Education -0.8624 0.1448 -5.954 3.66e-07
##
## Residual standard error: 9.446 on 45 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.4406, Adjusted R-squared: 0.4282
## F-statistic: 35.45 on 1 and 45 DF, p-value: 3.659e-07
##
## Next step: Use 'setx' method
The -0.86 coefficient on education suggests a negative relationship
between the education of a province and its fertility rate. More
precisely, for every one percent increase in draftees educated beyond
primary school, the fertility rate of the province decreases 0.86 units.
To help us better interpret this finding, we may want other quantities
of interest, such as expected values or first differences. Zelig makes
this simple by automating the translation of model estimates into
interpretable quantities of interest using Monte Carlo simulation
methods (see King, Tomz, and Wittenberg (2000) for more information).
For example, let’s say we want to examine the effect of increasing the
percent of draftees educated from 5 to 15. To do so, we set our
predictor value using the setx() and setx1() functions:
# set education to 5 and 15
z5_1 <- setx(z5_1, Education = 5)
z5_1 <- setx1(z5_1, Education = 15)
# model summary
summary(z5_1)
## setx:
## (Intercept) Education
## 1 1 5
## setx1:
## (Intercept) Education
## 1 1 15
##
## Next step: Use 'sim' method
After setting our predictor value, we simulate using the sim() method:
# run simulations and estimate quantities of interest
z5_1 <- sim(z5_1)
# model summary
summary(z5_1)
##
## sim x :
## -----
## ev
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## 1 75.30616 1.658283 75.28057 72.12486 78.48007
## pv
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## [1,] 75.28028 9.707597 75.60282 57.11199 94.3199
##
## sim x1 :
## -----
## ev
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## 1 66.66467 1.515977 66.63699 63.66668 69.64761
## pv
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## [1,] 66.02916 9.441273 66.32583 47.19223 82.98039
## fd
## mean sd 50% 2.5% 97.5%
## 1 -8.641488 1.442774 -8.656953 -11.43863 -5.898305
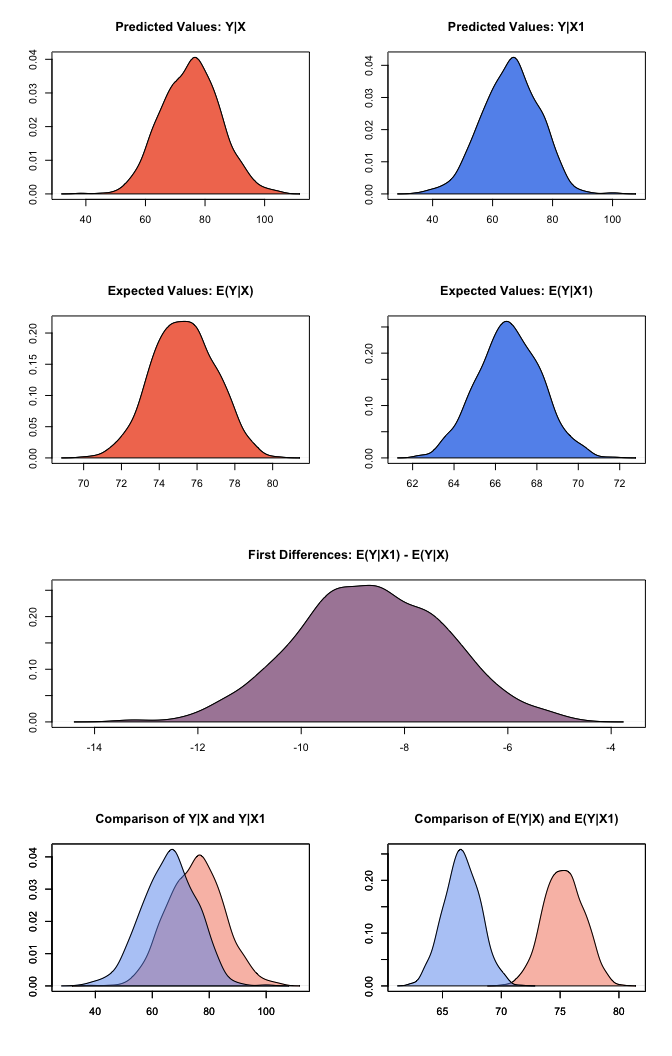
At this point, we’ve estimated a model, set the predictor value, and
estimated easily interpretable quantities of interest. The summary()
method shows us our quantities of interest, namely, our expected and
predicted values at each level of education, as well as our first
differences–the difference in expected values at the set levels of
education.
Visualizations
Zelig’s plot() function plots the estimated quantities of interest:
plot(z5_1)
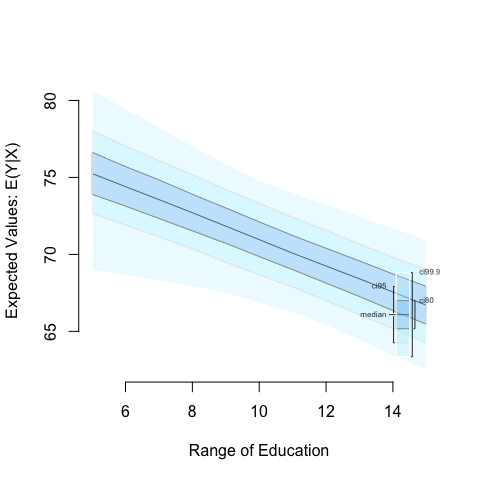
We can also simulate and plot simulations from ranges of simulated values:
z5_2 <- zelig(Fertility ~ Education, model = "ls", data = swiss, cite = FALSE)
# set Education to range from 5 to 15 at single integer increments
z5_2 <- setx(z5_2, Education = 5:15)
# run simulations and estimate quantities of interest
z5_2 <- sim(z5_2)
Then use the plot() function as before:
z5_2 <- plot(z5_2)
Getting help
The primary documentation for Zelig is available at: http://docs.zeligproject.org/articles/.
Within R, you can access function help using the normal ? function,
e.g.:
?setx
If you are looking for details on particular estimation model methods,
you can also use the ? function. Simply place a z before the model
name. For example, to access details about the logit model use:
?zlogit
Building Zelig (for developers)
Zelig can be fully checked and build using the code in check_build_zelig.R. Note that this can be time consuming due to the extensive test coverage.