A Virtual Optogenetics Laboratory
PyRhO is a Python module to fit, characterise and simulate (rhod)opsin photocurrents.
Background
Optogenetics has become a key tool for understanding the function of neural circuits and controlling their behaviour. An array of directly light driven opsins have been genetically isolated from several families of organisms, with a wide range of temporal and spectral properties. In order to characterize, understand and apply these rhodopsins, we present an integrated suite of open-source, multi-scale computational tools called PyRhO.
PyRhO enables users to:
- Characterize new (and existing) rhodopsins by automatically fitting a minimal set of experimental data to three, four or six-state kinetic models,
- Simulate these models at the channel, neuron & network levels and
- Gain functional insights through model selection and virtual experiments in silico.
The module is written in Python with an additional IPython/Jupyter notebook based GUI, allowing models to be fit, simulations to be run and results to be shared through simply interacting with a webpage. The seamless integration of model fitting algorithms with simulation environments for these virtual opsins (including NEURON and Brian2) will enable (neuro)scientists to gain a comprehensive understanding of their behaviour and rapidly identify the most suitable variant for application in a particular biological system. This process may thereby guide not only experimental design and opsin choice but also alterations of the rhodopsin genetic code in a neuro-engineering feed-back loop. In this way, we hope PyRhO will help to significantly improve optogenetics as a tool for transforming biological sciences.
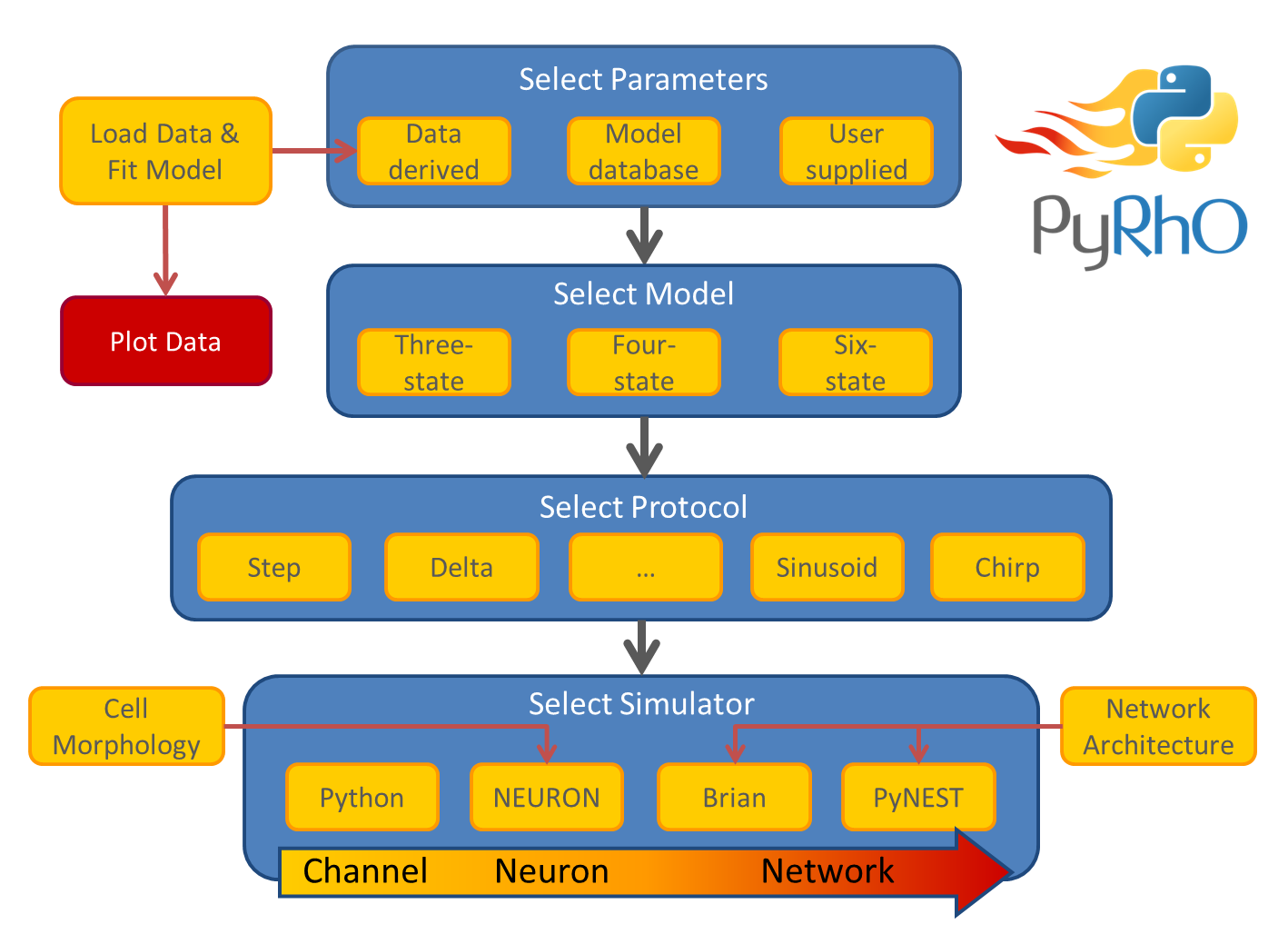
Architecture
PyRhO is composed of several abstraction layers, including the Model layer, Protocol layer and Simulator layer (shown in the architectural schematic below). Choices in each layer are independent or one another, giving a large number of possible combinations to suit many needs for in silico experiments. Additionally, parameters may be fit to each type of kinetic model from experimental data or loaded from the default options of popular opsins.
Prometheus
If you would like to try PyRhO before installing it, go to try.projectpyrho.org to launch a fully configured Jupyter notebook in your browser.
Docker
If you wish to use PyRhO in a Docker container, a Dockerfile is provided in the accompanying Prometheus repository: https://github.com/ProjectPyRhO/Prometheus
The Dockerfile will build a full installation including the NEURON and Brian2 simulators and the Jupyter notebook GUI. See the repository's README file for instructions.
Installation
To install PyRhO (including the GUI) from PyPI use the command: :
pip install pyrho[full]
Alternatively, to install the latest code from GitHub (including the GUI) use the command: :
pip install git+https://github.com/ProjectPyRhO/PyRhO.git#egg=PyRhO[full]
To use PyRhO with the NEURON simulator in a Python 3 environment, NEURON must be compiled from its source code. An installation script is provided for doing this on Mac OS X or Linux. The resultant installation will also work with Python 2. If you only wish to use PyRhO/NEURON with Python 2 however, a standard NEURON installation should be sufficient. The shell script may be called after importing PyRhO with the following function: :
from pyrho import *
setupNEURON('/installation/path/for/NEURON/')
This will attempt to compile NEURON from source, copy the supplied mod
and hoc files into place (the current working directory by default)
finally compiling the mod files describing the opsin models ready for
inclusion in simulations.
The Brian simulator is included with the PyRhO installation for modelling networks of optogenetically transfected spiking neurons.
Further Information
If you use PyRhO please cite our paper:
Evans, B. D., Jarvis, S., Schultz, S. R. & Nikolic K. (2016) "PyRhO: A Multiscale Optogenetics Simulation Platform", Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 10 (8). doi:10.3389/fninf.2016.00008
@ARTICLE{pyrho,
AUTHOR={Evans, Benjamin D. and Jarvis, Sarah and Schultz, Simon R. and Nikolic, Konstantin},
TITLE={PyRhO: A Multiscale Optogenetics Simulation Platform},
JOURNAL={Frontiers in Neuroinformatics},
VOLUME={10},
YEAR={2016},
NUMBER={8},
URL={http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fninf.2016.00008/full},
DOI={10.3389/fninf.2016.00008}
}
The PyRhO project website with additional documentation may be found here: www.imperial.ac.uk/bio-modelling/pyrho
Finally, don't forget to follow us on twitter for updates: @ProjectPyRhO!