brainreg
brainreg is an update to amap (itself a port of the original Java software) to include multiple registration backends, and to support the many atlases provided by bg-atlasapi.
Documentation can be found here and a tutorial is here. For segmentation of bulk structures in 3D space (e.g. injection sites, Neuropixels probes), please see brainreg-segment.
N.B. There is also a napari plugin if you'd rather use brainreg with a graphical user interface. Currently this interface is slightly limited compared to the command line tool
This software is at a very early stage, and was written with our data in mind. Over time we hope to support other data types/formats. If you have any issues, please get in touch on the forum or by raising an issue.
Details
The aim of brainreg is to register the template brain (e.g. from the Allen Reference Atlas) to the sample image. Once this is complete, any other image in the template space can be aligned with the sample (such as region annotations, for segmentation of the sample image). The template to sample transformation can also be inverted, allowing sample images to be aligned in a common coordinate space.
To do this, the template and sample images are filtered, and then registered in a three step process (reorientation, affine registration, and freeform registration.) The resulting transform from template to standard space is then applied to the atlas.
Full details of the process are in the
original aMAP paper.
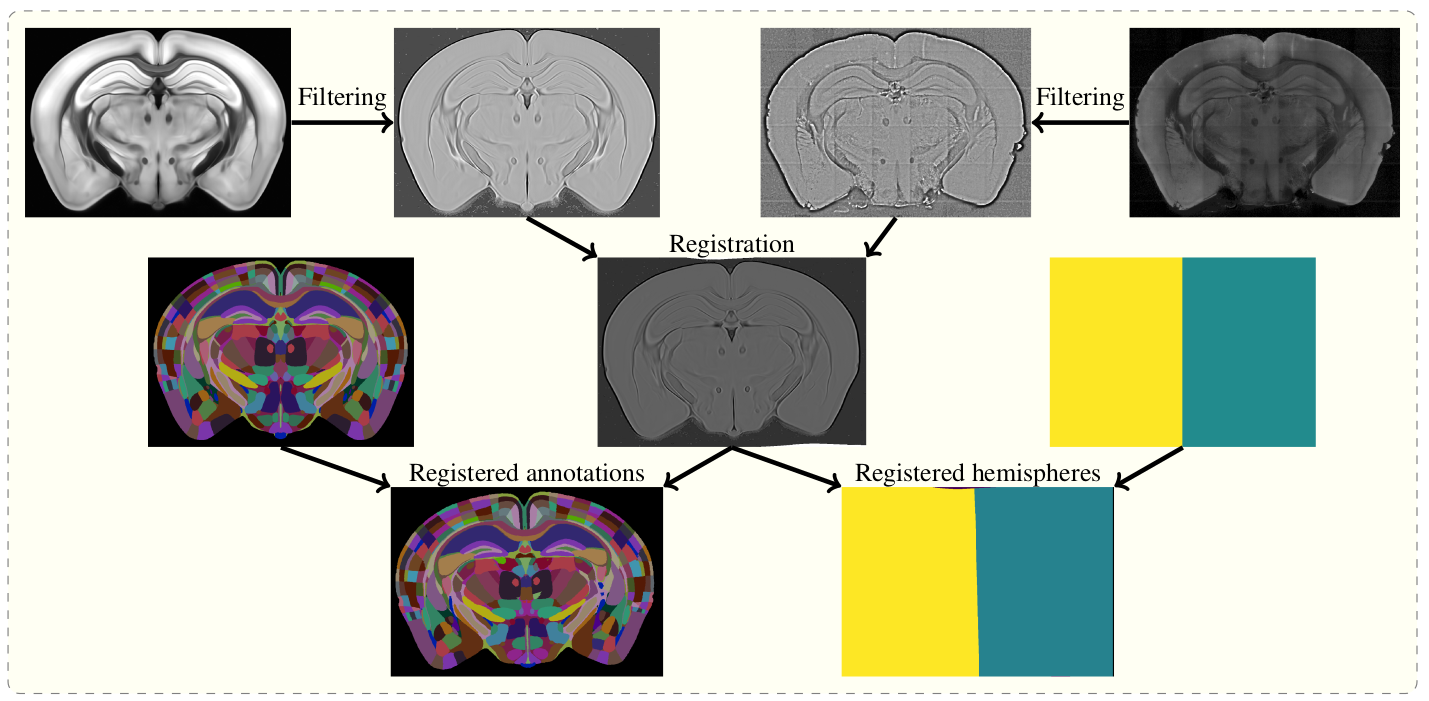
Overview of the registration process
Installation
pip install brainreg[napari]To only install the command line tool with no GUI (e.g. to run brainreg on an HPC cluster), just run:
pip install brainregN.B. If you are using macOS, please run conda install -c conda-forge niftyreg to ensure all dependencies are installed.
Usage
Basic usage
brainreg /path/to/raw/data /path/to/output/directory -v 5 2 2 --orientation pslArguments
Mandatory
- Path to the directory of the images. (Can also be a text file pointing to the files)
- Output directory for all intermediate and final results
You must also specify the voxel sizes, see Specifying voxel size
Additional options
-aor--additionalPaths to N additional channels to downsample to the same coordinate space.--sort-input-fileIf set to true, the input text file will be sorted using natural sorting. This means that the file paths will be sorted as would be expected by a human and not purely alphabetically.--brain_geometryCan be one offull(default) for full brain registration,hemisphere_lfor left hemisphere data-set andhemisphere_rfor right hemisphere data-set.
Misc options
--n-free-cpusThe number of CPU cores on the machine to leave unused by the program to spare resources.--debugDebug mode. Will increase verbosity of logging and save all intermediate files for diagnosis of software issues.--save-original-orientationOption to save the registered atlas with the same orientation as the input data.
Atlas
By default, brainreg will use the 25um version of the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas. To use another atlas (e.g. for another species, or another resolution), you must use the --atlas flag, followed by the string describing the atlas, e.g.:
--atlas allen_mouse_50umTo find out which atlases are available, once brainreg is installed, please run brainglobe list. The name of the resulting atlases is the string to pass with the --atlas flag.
Registration backend
To change the registration algorithm used, use the --backend flag. The default is niftyreg as that is currently the only option.
Input data orientation
If your data does not match the brainglobe default orientation (the origin voxel is the most anterior, superior, left-most voxel, then you must specify the orientation by using the --orientation flag. What follows must be a string in the bg-space "initials" form, to describe the origin voxel.
If the origin of your data (first, top left voxel) is the most anterior, superior, left part of the brain, then the orientation string would be "asl" (anterior, superior, left), and you would use:
--orientation aslRegistration options
To change how the actual registration performs, see Registration parameters
Full command-line arguments are available with brainreg -h, but please
get in touch if you have any questions.
Visualisation
brainreg comes with a plugin (brainglobe-napari-io) for napari to view your data
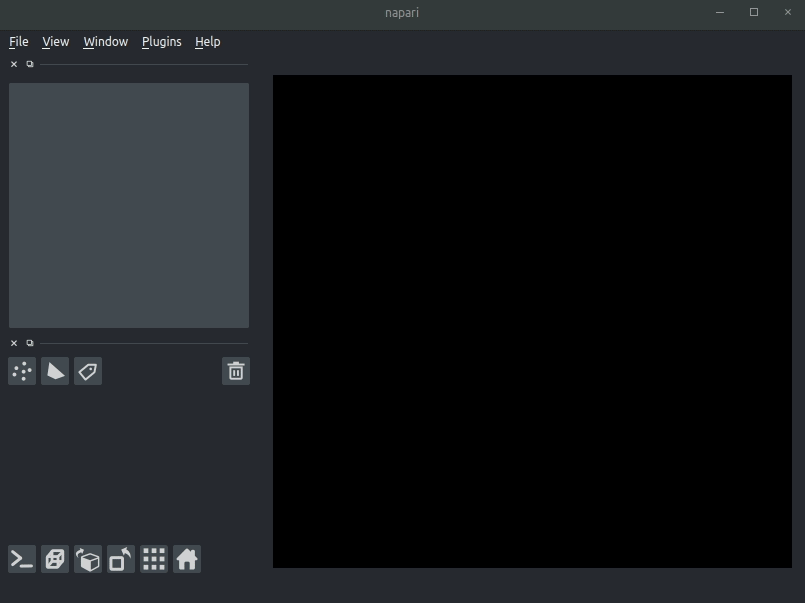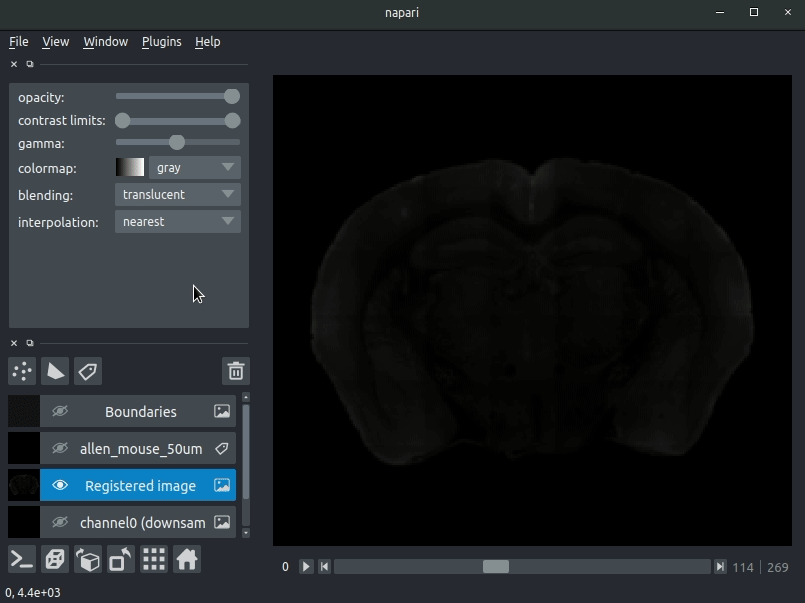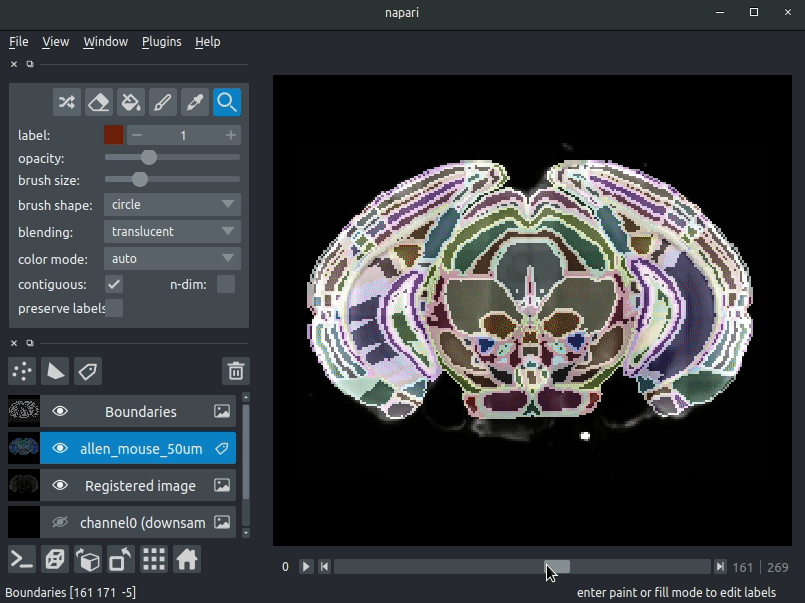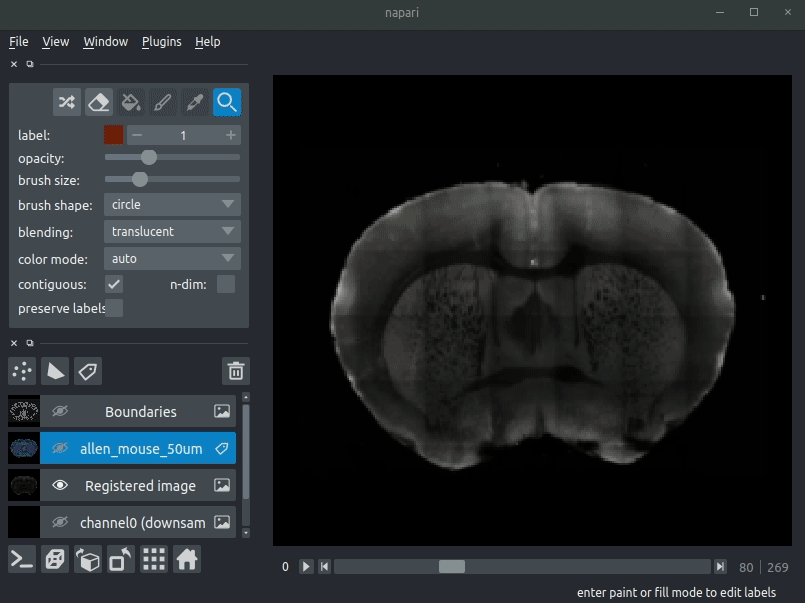
Sample space
Open napari and drag your brainreg output directory (the one with the log file) onto the napari window.
Various images should then open, including:
Registered image- the image used for registration, downsampled to atlas resolutionatlas_name- e.g.allen_mouse_25umthe atlas labels, warped to your sample brainBoundaries- the boundaries of the atlas regions
If you downsampled additional channels, these will also be loaded.
Most of these images will not be visible by default. Click the little eye icon to toggle visibility.
N.B. If you use a high resolution atlas (such as allen_mouse_10um), then the files can take a little while to load.
Atlas space
napari-brainreg also comes with an additional plugin, for visualising your data
in atlas space.
This is typically only used in other software, but you can enable it yourself:
- Open napari
- Navigate to
Plugins->Plugin Call Order - In the
Plugin Sorterwindow, selectnapari_get_readerfrom theselect hook...dropdown box - Drag
brainreg_standard(the atlas space viewer plugin) abovebrainreg(the normal plugin) to ensure that the atlas space plugin is used preferentially.
Contributing
Contributions to brainreg are more than welcome. Please see the contributing guide.
Citing brainreg
If you find brainreg useful, and use it in your research, please let us know and also cite the paper:
Tyson, A. L., Vélez-Fort, M., Rousseau, C. V., Cossell, L., Tsitoura, C., Lenzi, S. C., Obenhaus, H. A., Claudi, F., Branco, T., Margrie, T. W. (2022). Accurate determination of marker location within whole-brain microscopy images. Scientific Reports, 12, 867 doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-04676-9
Please also cite aMAP (the original pipeline from which this software is based):
Niedworok, C.J., Brown, A.P.Y., Jorge Cardoso, M., Osten, P., Ourselin, S., Modat, M. and Margrie, T.W., (2016). AMAP is a validated pipeline for registration and segmentation of high-resolution mouse brain data. Nature Communications. 7, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11879
Lastly, if you can, please cite the BrainGlobe Atlas API that provided the atlas:
Claudi, F., Petrucco, L., Tyson, A. L., Branco, T., Margrie, T. W. and Portugues, R. (2020). BrainGlobe Atlas API: a common interface for neuroanatomical atlases. Journal of Open Source Software, 5(54), 2668, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02668
Don't forget to cite the developers of the atlas that you used (e.g. the Allen Brain Atlas)!
The BrainGlobe project is generously supported by the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre and the Institute of Neuroscience, Technical University of Munich, with funding from Wellcome, the Gatsby Charitable Foundation and the Munich Cluster for Systems Neurology - Synergy.